20.04.2023 International Economics#
Learning Objectives:
international and domestic economic issues
recurring themes
trade / monetary distinguish
International Economics: How nations interact trough trade (of goods and services) and finance (flows of money and investment)
History of Trade:
Gravity Model#
How much do people trade with each other?
A = constant term
D = Distance
Y = GDP of respective country
Anomalies: (EU and US)
Ireland = cultural affinity
Netherlands = transport cost advantages
=> more Trade than predicted
other Aspects (not in Model):
cultural affinity
geography
Multinational Corps.
Borders
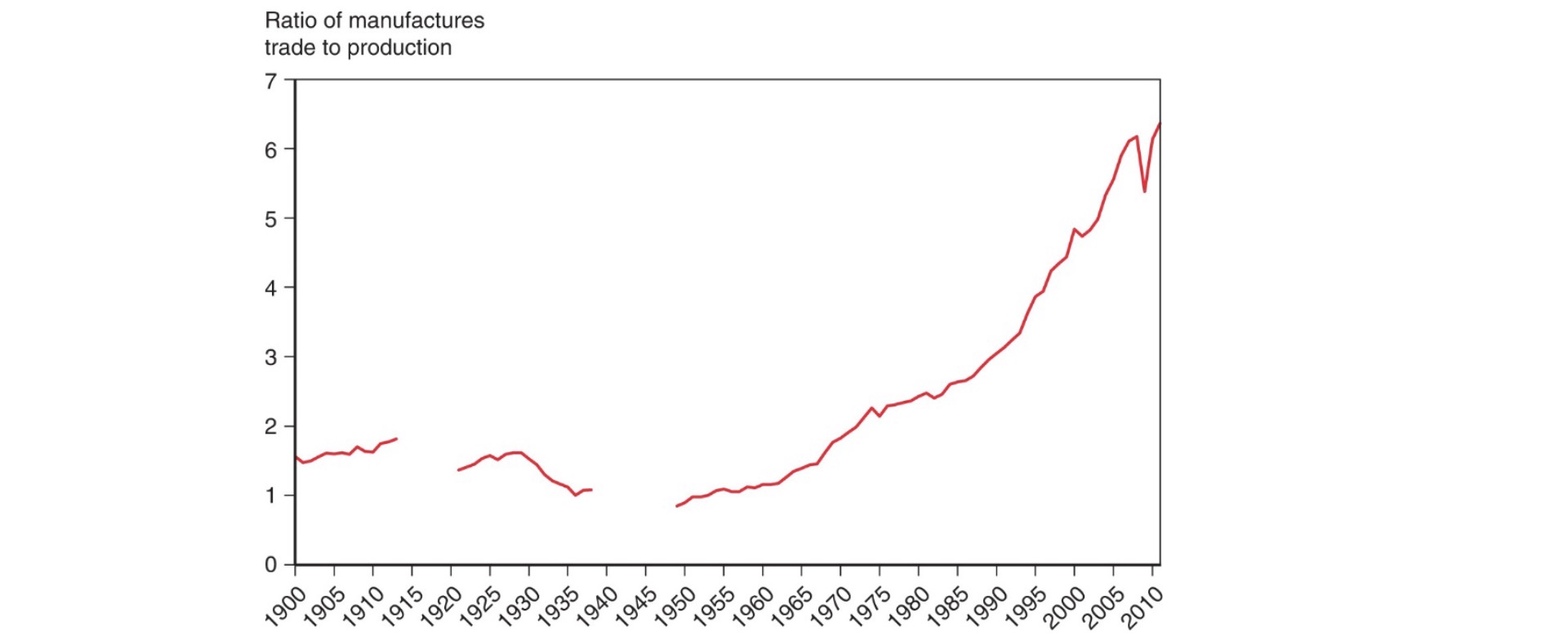
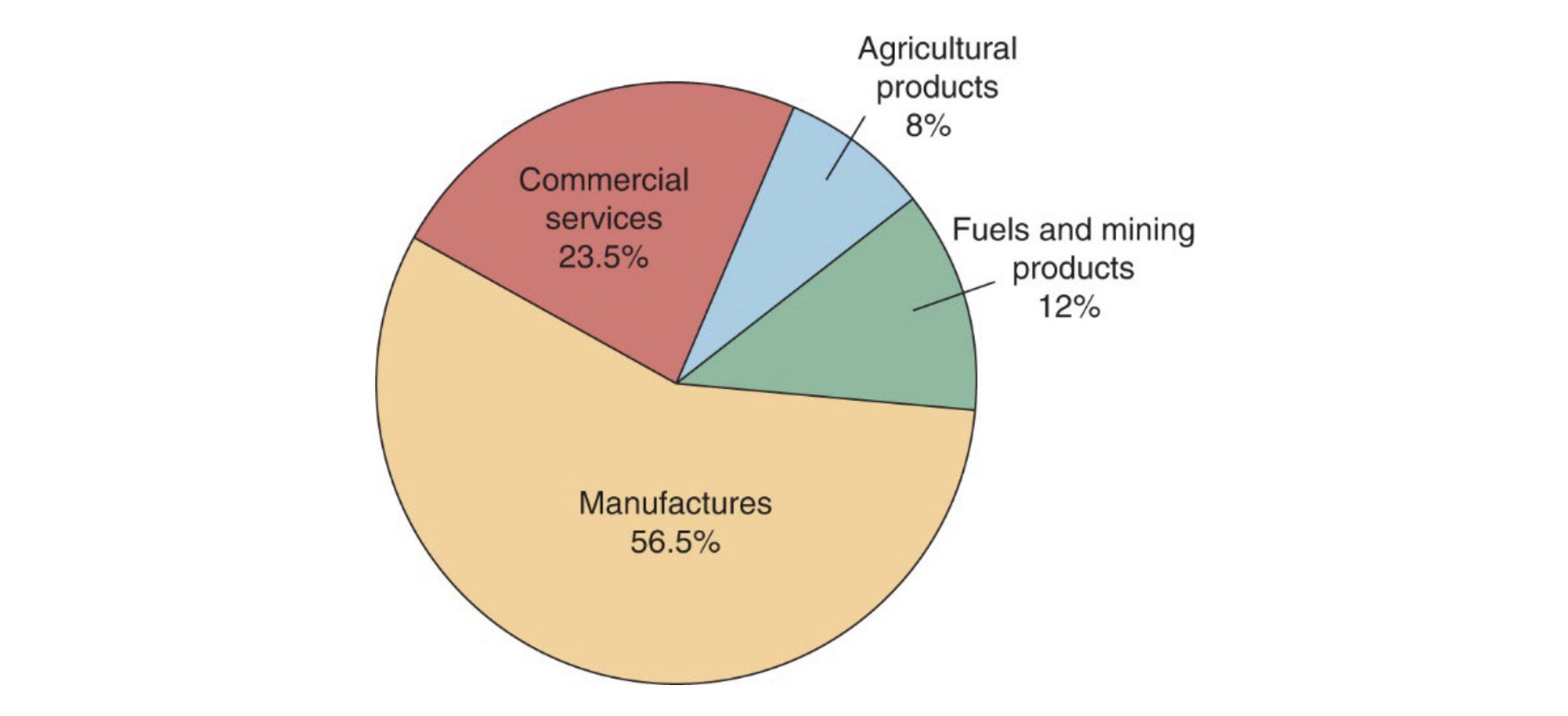
Trade Products#
mostly manufactured goods
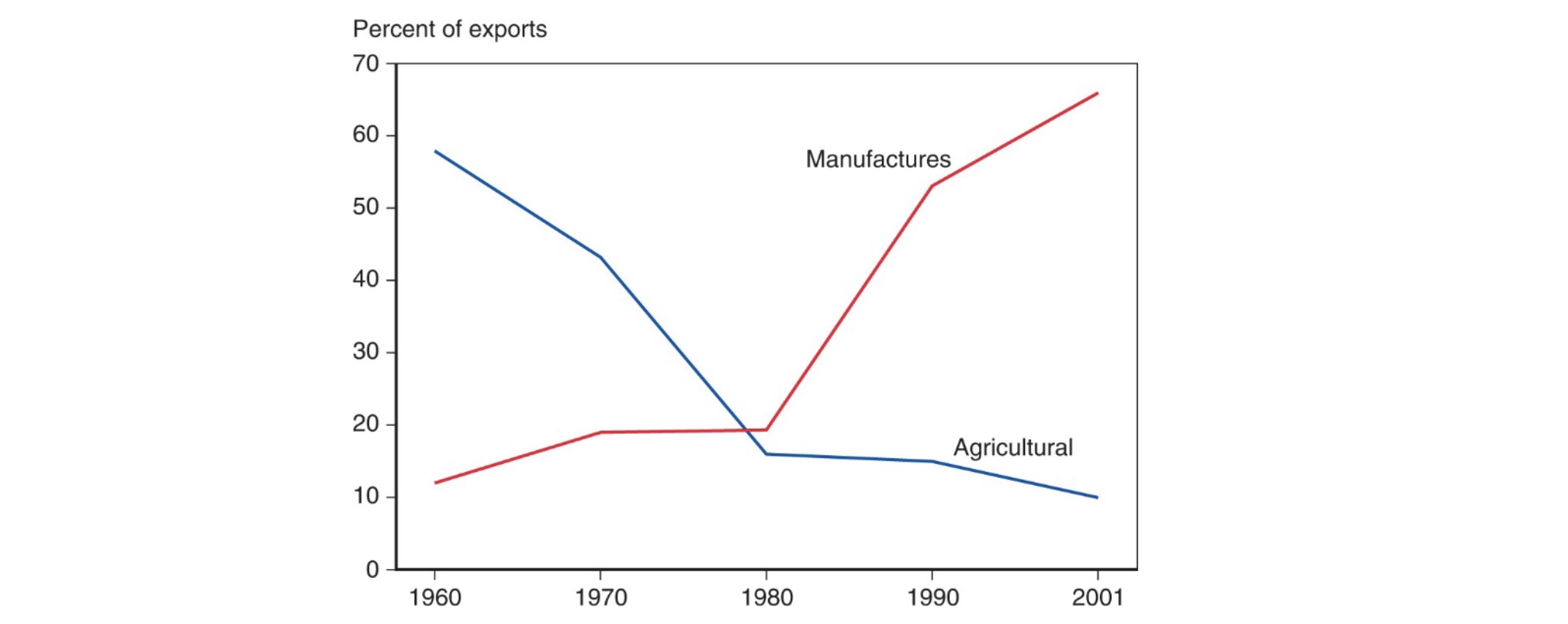
changes especially in developing countries:
historical: agricultural products
now: manufactured goods
Service Outsourcing#
in US, currently not significant
most jobs are not tradable
the tradable jobs are still often in the US
Exercise I:#
Exam:
Derivatives (basic calculus)
graphs
60 Minutes
Supply and Demand#
Supply: \(p = 0,5x +20\)
Demand: \(p = -0,75x+50\)
Ueqilibrium: \(x = 24, p=32\)
Interventions:
Government Minimum Price: \(p = 38\)
Demand: \(-12 = -0,75x \to x = 16\)
Fixed cost increases: new Supply: \(0,5x+30\)
new Equilibrium: \(x = 16, p=38\)
government demand subsidys: \(p = -x+50\)
new eq.: \(x= 20, p = 30\)
International Trade#
Degree of Openness: \(\frac{exports+imports}{GDP}*100\%\)
World Economy is concentrated in Europe / North America / Southeast Asia
Types of Trade#
Intraregional Trade
between partners of economic integration space (EU, NAFTA)
Interregional Trade
between different spaces / countries
GDP#
Calculation: Private Con+ Governemnt Con + Investments + Exports - Imports