08.05.2023 Economic Fluctuations#
Recessions and Unemployment#
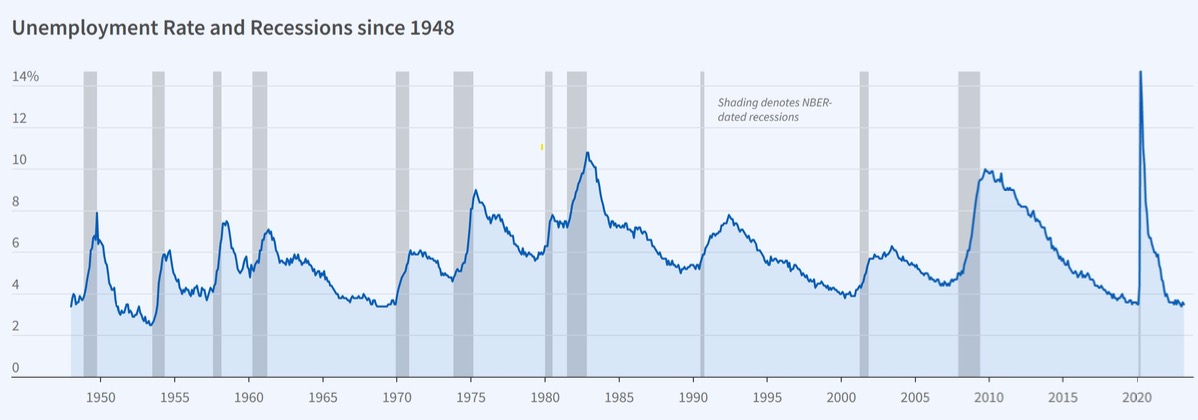
Connection between GDP and unemplyoment
but not always
downturn GDP => higher unemployment
=> described empirically in Okuns Law
two Definitions of Recession
NBER: period between peak and lowest point of economic activity
significant decline in econ. activity
economy-wide
alterantive: economic output level below normal level
possbile even during growth
until prevous output reached
Business Cycle#
Business Cycle: type of fluctuation (in capitalist economies) of aggregate economic activity between expansion / contraction
recurrent but not periodic
duration from one year to twelve years
Measurig aggregate Economy#
by measuirng GDP
Demand / Spending (households, firms, government…)
Production (value added)
Income (wages, profits…)
Flaws in GDP:
products not sold (care-arbeit)
environmental costs not included
Smooth Consumption#
People want smooth consumption
To have similiar quality of life
e.g pensions for elderly
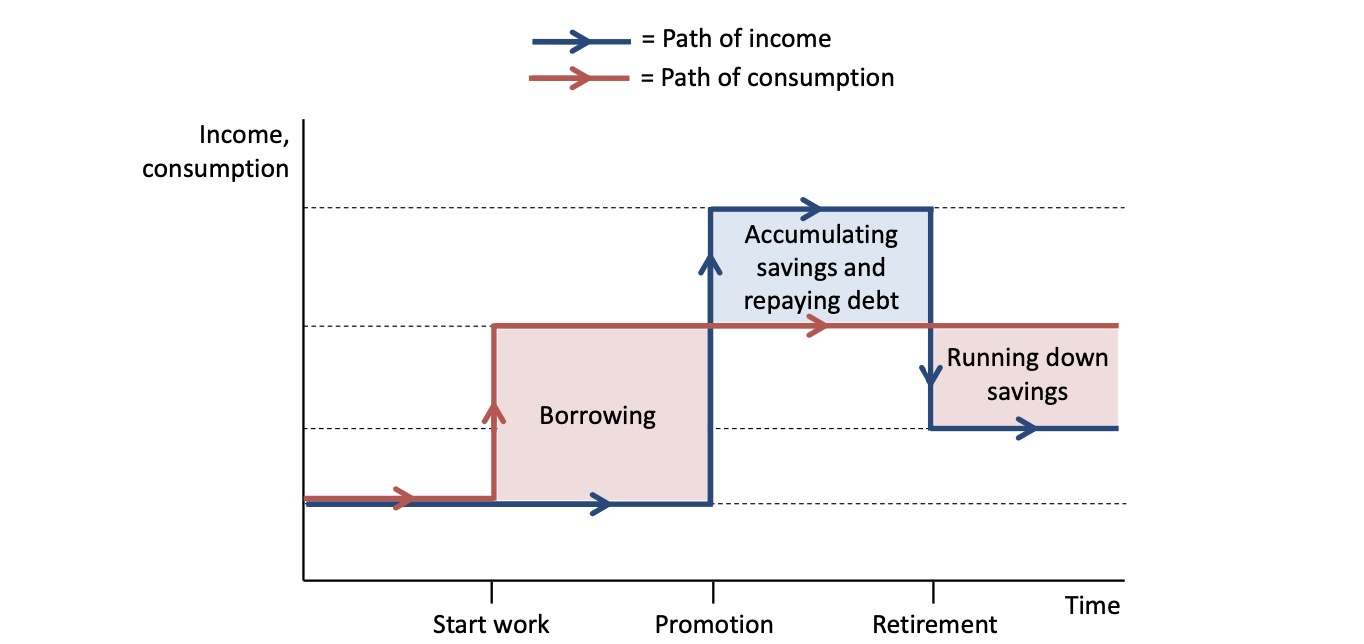
Smoothing via borrowing/lending/saving
Limits to shooting:
credit constraint
weakness of will
limited co-insurance
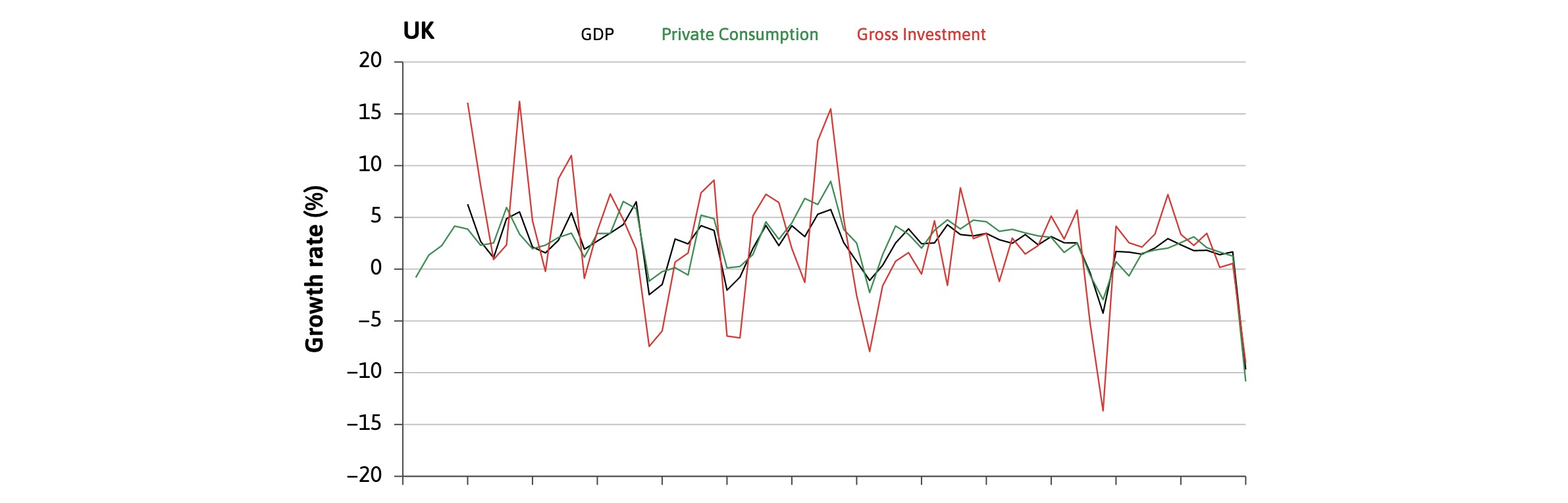
Volatile Investment#
Why is Investment volatile?
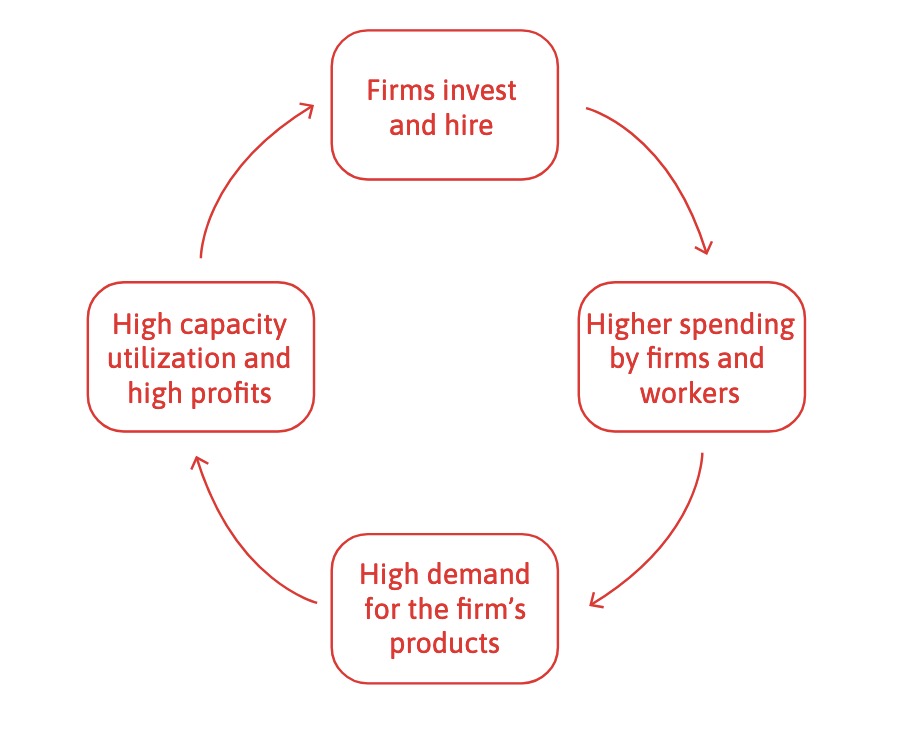
in Expansion: everybody wants to invest
wages rise = high demand for goods
firms produce more to saturate demand
optimistic future
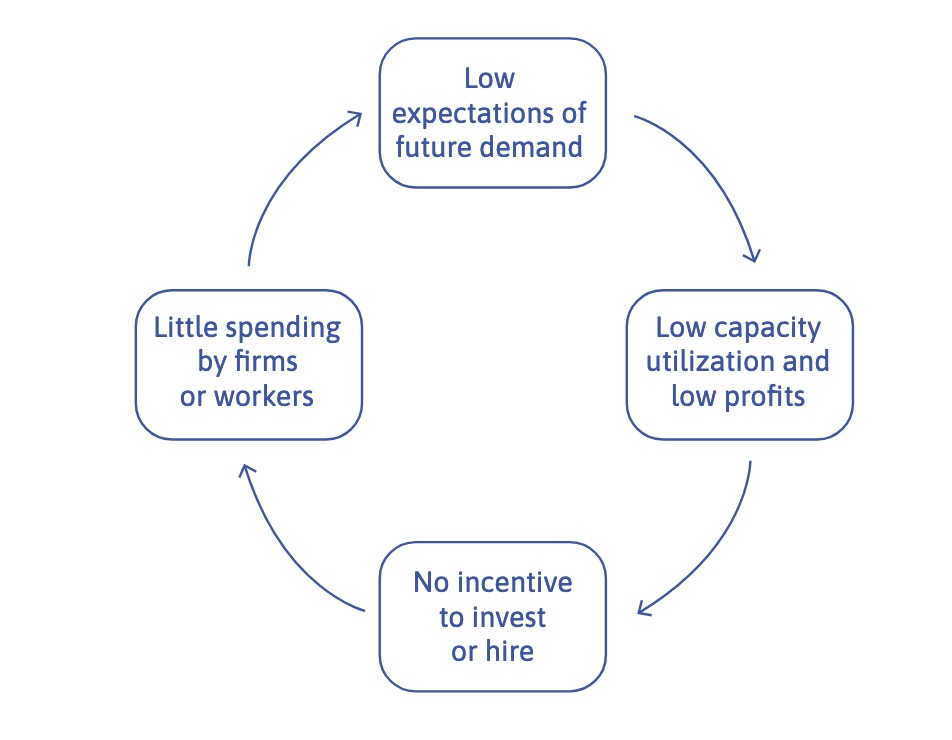
in Contraction: nobody invests, pessimistic future
=> Vicious Cycles
Contraction |
Expansion |
|---|---|
|
|
leads to self-enforcing business cycles
Symmetric Moving Average#
a mathematic filter to extract cycle from trend
symmetric: take last values in future and past
moving average: calculate for every time point
Example: \(y_{t} = x_{t-1}+x_{t}+x_{t+1}\)
Government Expenditure#
less volative
because not influenced by business confidence
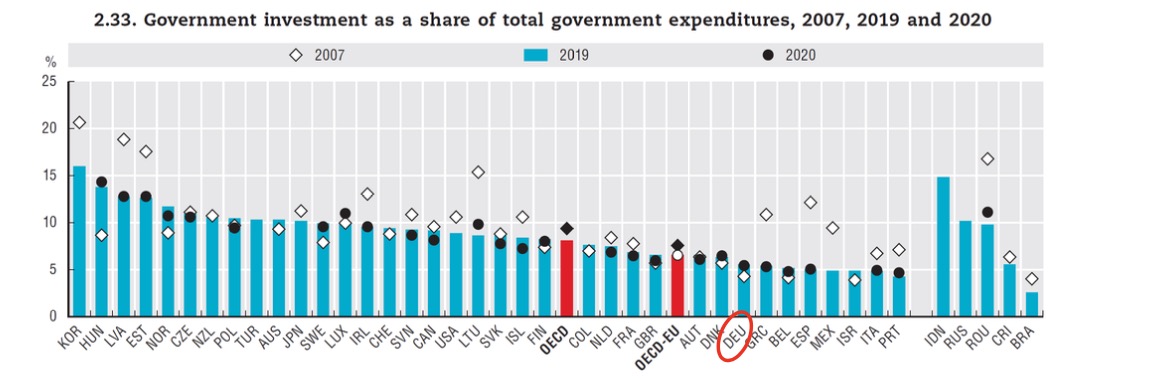
relatively low in Germany: aua
Trade Deficit#
What does it mean:
more imports than exports
saving less than investing
Interpretations
booming economy: higher demand than local production :thumbsup:
foreigners invest in country :thumbsup:
no need for saving for higher investing :thumbsup:
flow abroad of divididends :thumbsdown:
Remember:
the money used for foreing trade
is reinvested in the country (I > S)
Inflation#
Inflation: Increase in the general Price level in economy
measured by Consumer Price Index (CPI)
based on representative basket
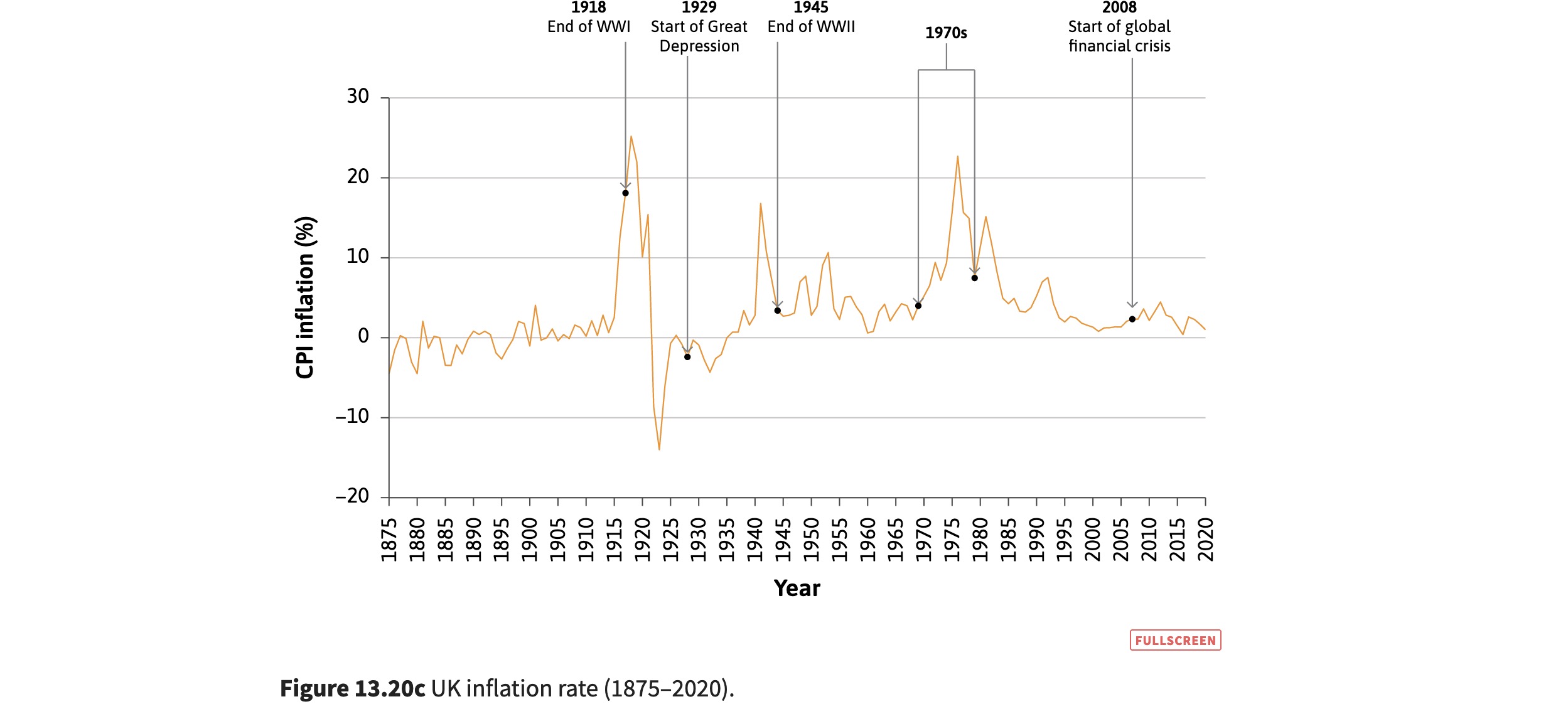
historic inflation
GDP-Deflator: implicit measure $\( p_t^{implicit} = \frac{nominal\ GDP_t}{real \ GDP_{t-base}} \)$
real GDP = use prices of last year
nominal GDP = prices of this year