25.10.2023 Tools II#
Randomized Control Trials#
Gold Standard to find out about causation
2 random groups
one treatment group, one with placebo
solvest the problem of bias
Bias: source of difference between treatment and control group that is correlated with the treatment but not due to the t.
Example: SAT Courses
Students taking SAT Prep Courses
have lower grades in the end
but due to lower starting point for course takers
Problems of RCT:
external validity: not applicable to other contexts
Attrition: reduction of sample size over time leads to bias
Expense
RCT in TANF context#
Experiment in Califarion in 1992
1/3 families to existing program
2/3 treatment group with 15% lower benefits
Results
Employment rates: 49% vs 44.5%
Elasticity of Labor: \(\frac{ -10\% }{15\%}=0.67\)
Observational Data#
Obersavtional Data: Data generated by individual behavior in real world
Problem: Bias
Time Series Analysis#
Analysis of the co-movement of two trends
can be used to analyze correltaion
to support theory
TANF Example
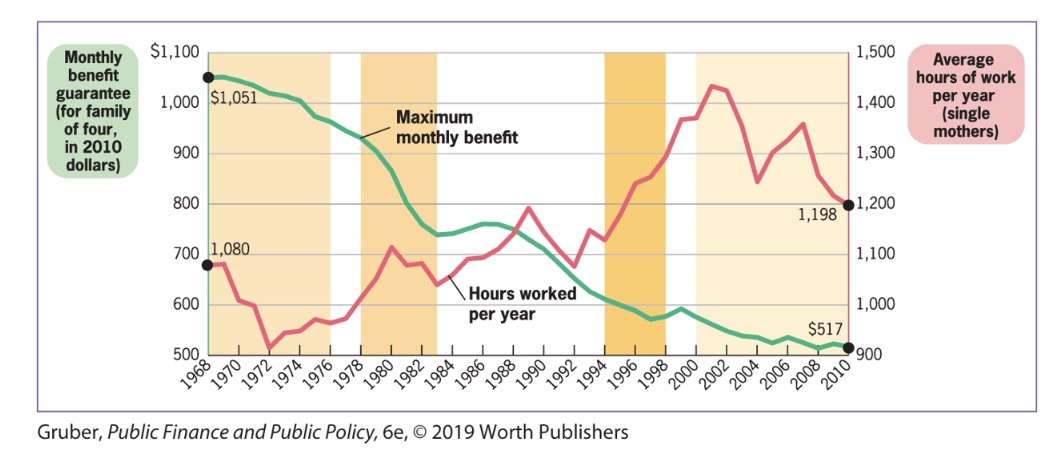
Problems:
separation from correlation to causation
excldued variables (often macro labor market)
Regression Analysis#
= best fitting linear-relationship between two variables
Cross-sectional regression analysis: Statistical analysis of the relationship between two or more variables exhibited by many individuals at one point in time.
find best fitting linear elationship between two variables
Regression line: The line that measures the best linear approximation to the relationship between any two variables
Example:
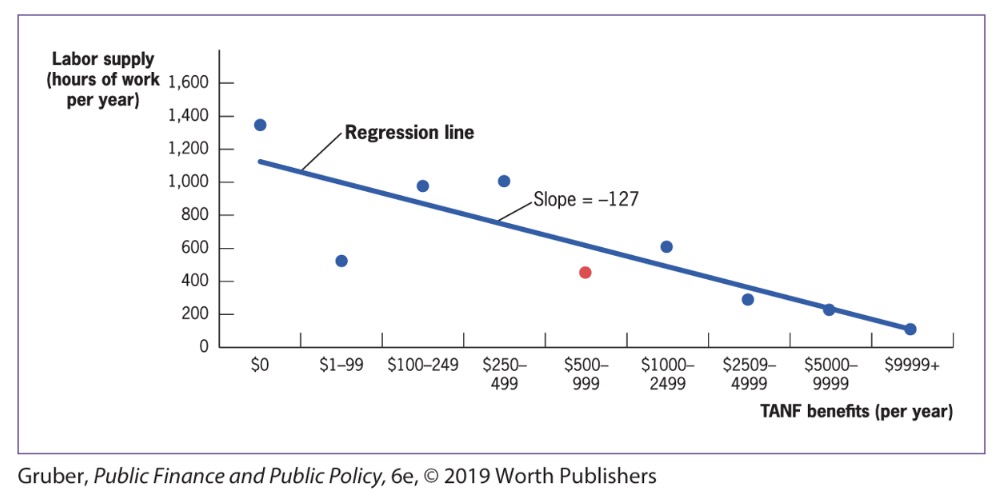
Problem of Biases can be solved with control variables
Control Variables: Variables that are included in cross-sectional regression models to account for differences between treatment and control groups that can lead to bias
Quasi Experiments#
Quasi Experiments: Changes in economic environment that create nearly identical treatment and control groups for studying the effect of that environmental change
Example: Card minimum wage Research uses DiD
Difference in Difference (DiD): The difference between the changes in outcomes for the treatment group and control group
Hypothetical Example: one state increases state aid, other does not
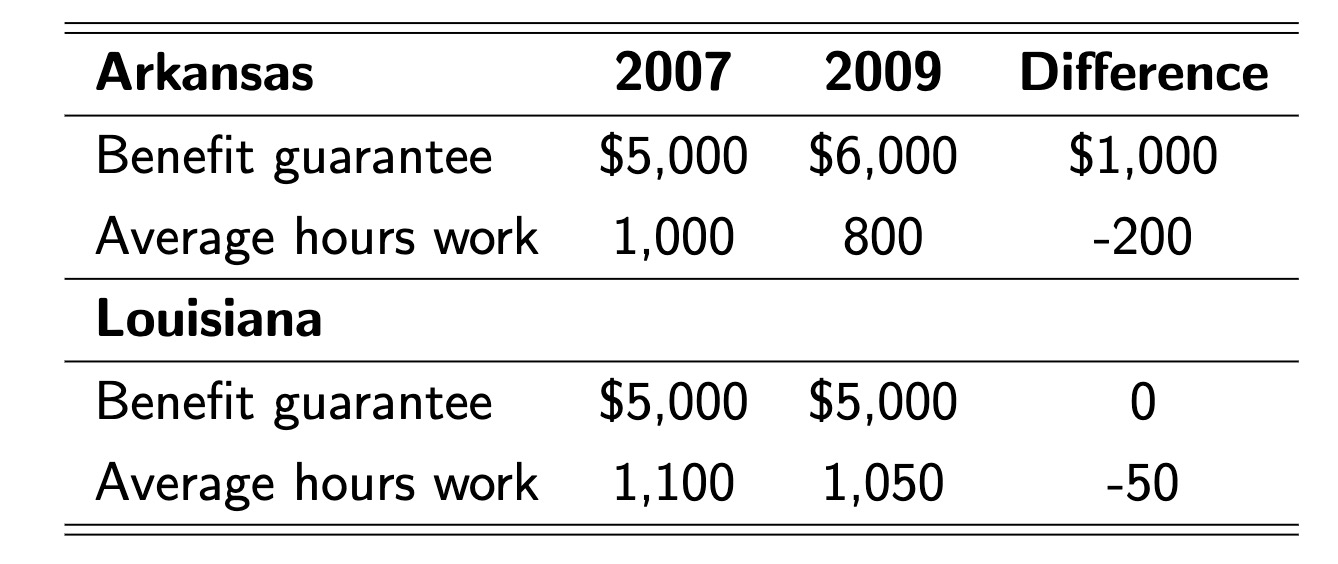
Assumption:
external effects (financial crisis) affect both states in the same way
both groups would develop the same (common trend assumption)
Tutorial#
internal validity: how valid for the population being studied
external validity: how valid for the general population
Threats to external validiry
non representative sample
non represenattive treatment
general equilibrium
scale and duration might change economic environment
ex: training unemployed => higher expectations from employers
changes baseline
Regression#
= best fitting linear-relationship between two variables
just correlation!
selection bias, omitted-variable bias