25.04.2024 Schockindustrialisierung#
Ch. 5: Soviet Industrialization#
before Stalin
indsustries organized in trusts
pofit maximizing
price mechanism
after 1928
5 year plan
output maximizing
centralized prices
effects
no more cost control
soft budget constraint
target rarely met
labor ineffiency
only focus on marginal product of next worker
not marginal cost
target adjusted in view of performance
inefficient build up of reserves
Sectors#
Capital accumuliation trough
exporting grain (limited)
heavy industry prioritazition
underinvestment in housing etc
rapid acceleration of physical capital
Human Capital
before: low literacy, few higher ed.
studys then showd ROI on education
after 1928: universal ed, fast human capital accumulation
Agriculture
(forced) collectivization
extermination of kulak class (exile, expropriation)
income divided according to days worked
unpopular! silent protests
=> nationalization
1930s: mechanization
Industrialization
growth = 5.3% p.y
urban boom, rural suffering
farm output: 3x (28-1940)
iron output: 4x
consumer goods: 0.8x
due to bad collectivization of agricutlure (=input)
takes time
Urbanization:
city pop. growth: 2x (1928-1940)
demand side: higher wages
supply side: less work due to mechaniztaion in rural
forced labor supply in gulags
amenities not rise with pop
Ch. 8: Caused of Rapid Industrialization#
quantitative analysis with Simulation Model
Inputs: Agriculture, Labor, Capital
Sectors: producer goods, consumer goods, agriculture
Purchasers: State, urban Households, peasants
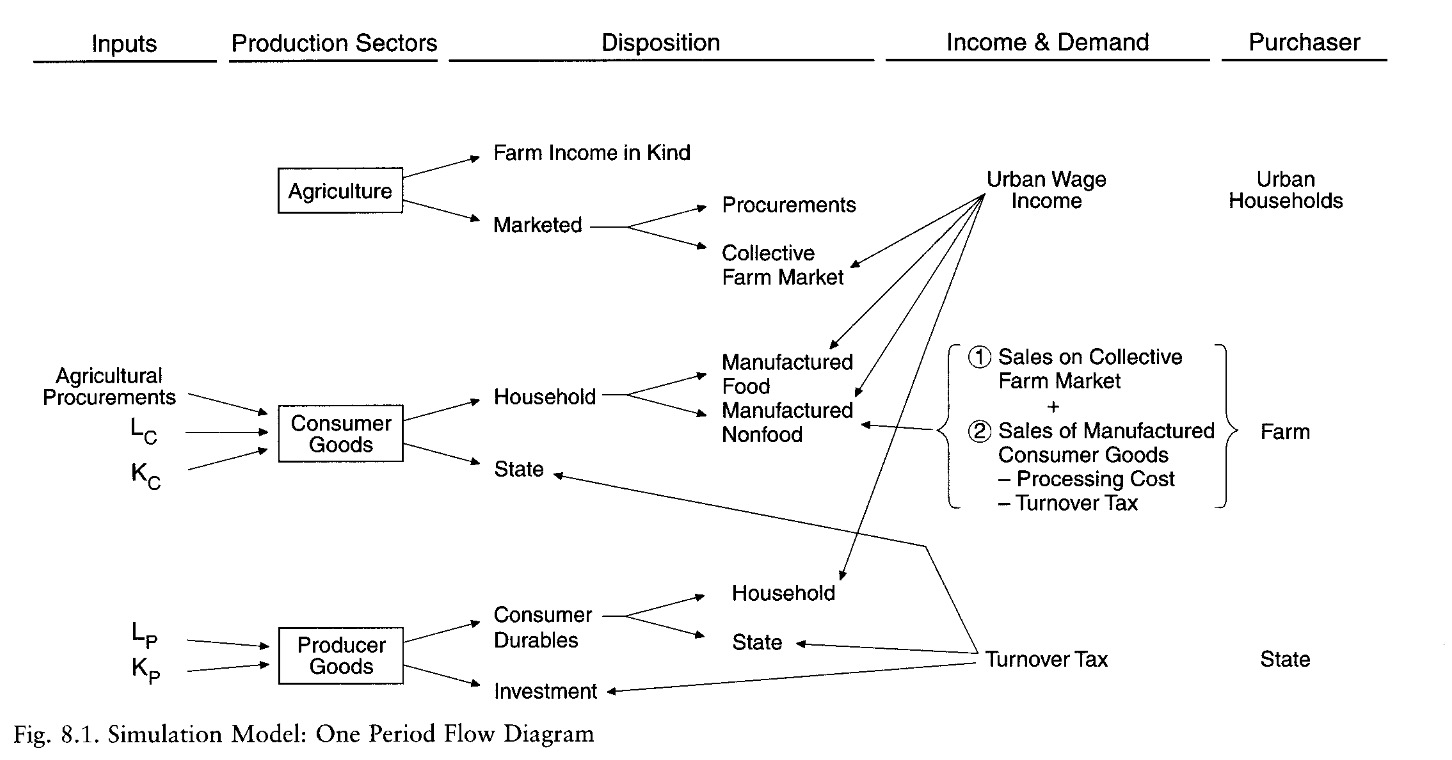
Simulation#
Capital = compounded from last year - consumption
labor supply = demographic model
1928-1940
3 Model Trajecotires
Collectivized (actual)
obligatory deliveries
turnover tax
antipeasant
NEP forward simulation
no collect.
market relationship urban-rural
capitalist
hard budget constraint
unemployment
Results#

Collectivized
highest value added at end of period
lower consumptio in middle, but higher afterward
spillover of growht from producer goods
hindered by 2.WW buildup of military , cost on investment
higher migration = more efficient
NEP
lower investment rates
but also no livestock deaths due to collectivization
general = lower value added comp. to coll.
but onyl slightly less GDp
due to more efficient agriculture
Capitalism
25% unemployment
probably large informal sector
worse performance overall
General
Agriculture Collectivization: small economic gains, large human misery!
structural unemployment = solved by soft budget constraint + high targets (keynesianismus)
NEP would have sufficed
export oriented strategy was not needed (grain etc.)
investment strategy + soft budget constraint => Soviet growth
Question: Financial Crisis in NEP / Capitalism Model?