18.10.2023 Tools of Public Economics#
Theoretical Framework#
Neoclassical / Mainstream Economics
good in predicting individual behavior
theory was updated with foundations from other schools of thought
Demand#
for Goods
Constraint Utility Maximization#
Assumption:
limited resources
individual has utility function
Aim = maximize welfare
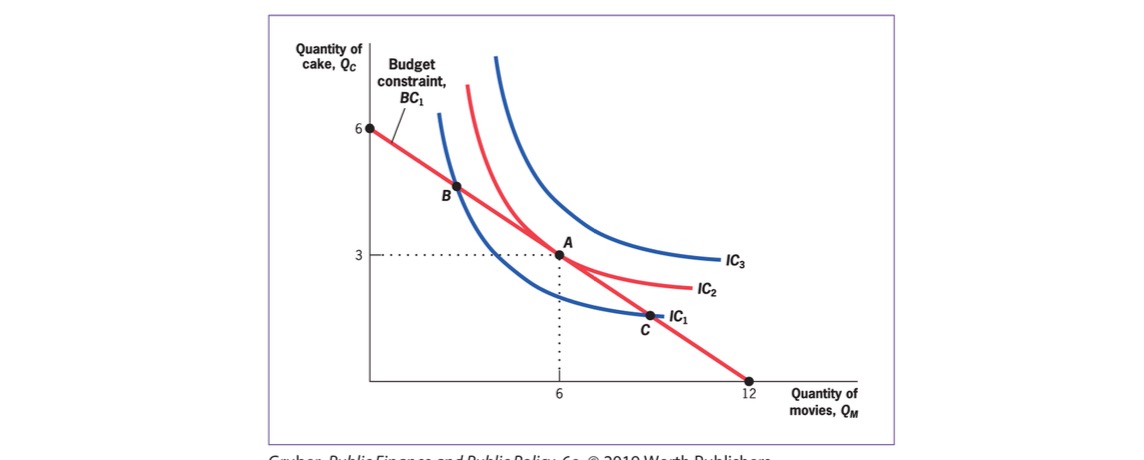
Indifference Curve: graphical Representation of bundles of goods that make qually well off
Underlying math: Utility Function
marginal utility = derivative, additional utility of one more
Diminishing Marginal Utility
Marginal Rate of Subst.: Willingness to trade one good for another, slope of IDC
Budget Constraint: $\( Y = P_C Q_C+P_MQ_M \)$
Price Changes#
can have two effects
Substitution Effect
Income Effect
Elasticity of Demand: % change in demand due to 1% increase in price
Supply#
Supply Curve = outcome of profit maximization
Production Function: \(q = \sqrt{K * L}\)
K = Capital
L = Labour
Profit Maximization at short term: \(p = MC\)
Equilibrium#
at Demand = Supply
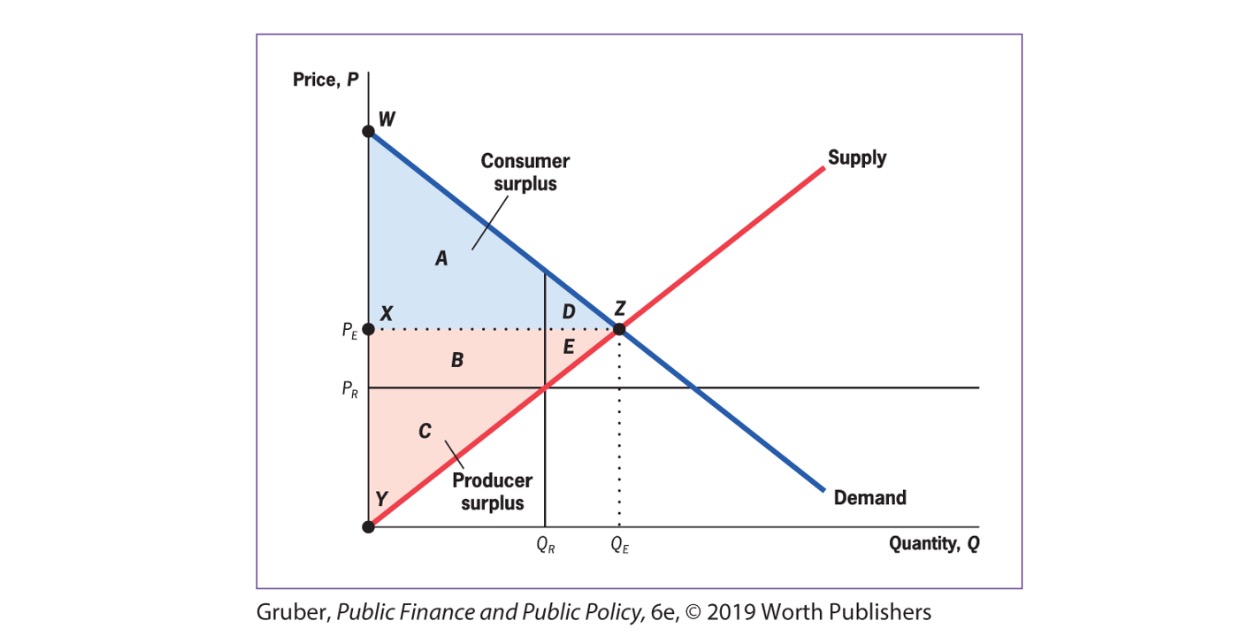
Theorems of Welfare Economics
The competitive equilibrium, where supply equals demand, maximizes social efficiency.
Society can attain any efficient outcome by suitably redistributing resources among individuals and then allowing them to trade freely.
under specific conditions!, that almost never exist (full information, no externalities?!)
Problem: Equity Effiency Tradeoff
Exercise#
2:#
Example Points:
P=10 => Q=150
P=5 => Q=200
Elasticity:
Elasticity is only local (for these 2 points)
3: Subsidy#
Government subsidizes firts 5 units of clothing to half of price $\( 100 = 4*Q_F+10*Q_C \)$
now two slopes
\(p_{clothing} = 5\) for \(Q_C \le 5\)
\(p_{clothing} = 10\) for \(Q_C > 5\)
Clothing Intercept now = 12.5
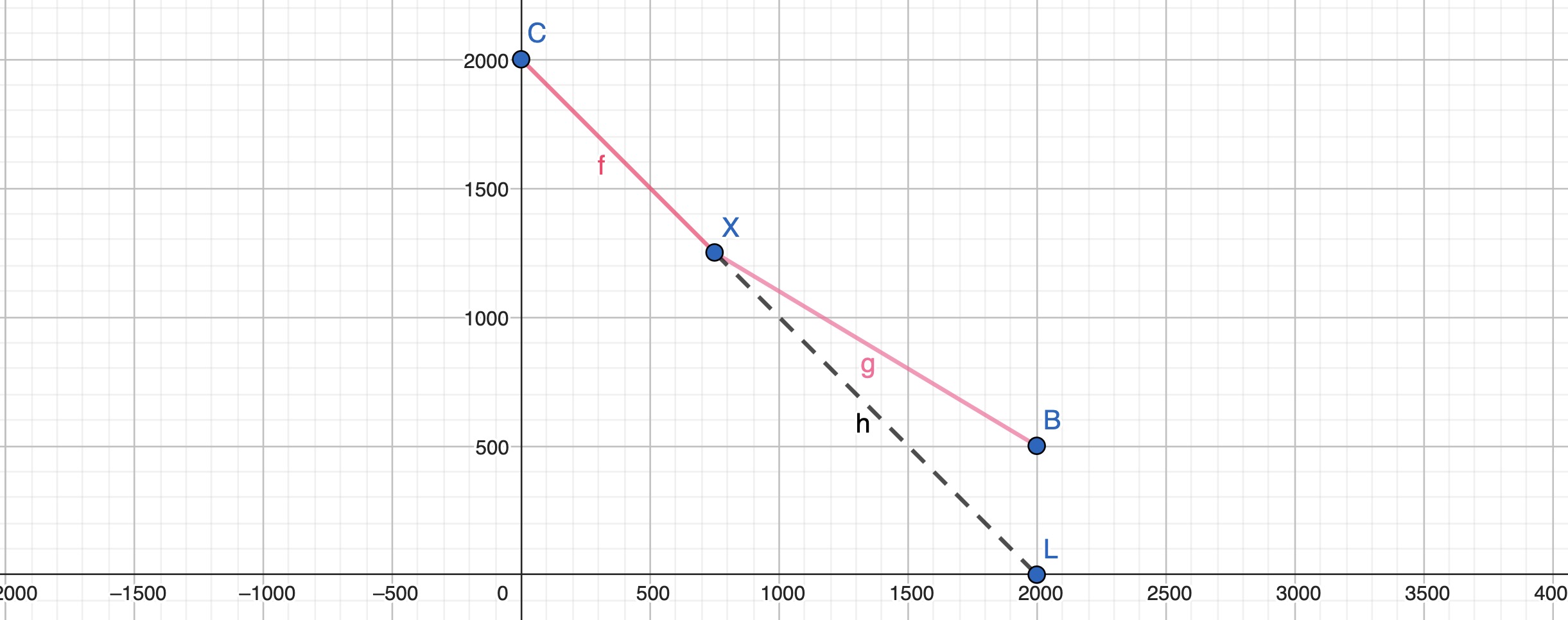
4: Income Program#
Work: 2000h at 10€
Benefit: 5000€
Benefit Reduction Rate = 40%
Kink Point (where you drop out of the program)
\(C*0,4 = 5000 \to C=12500\)
\(W=\frac{ 12500 }{10} = 1250\)
\(L=2000-1250 = 750\)
Graphic: