08.06.2024 Binary Variables#
Single Dummy Variable#
Binary Variable: represent qualitative factors in TRUE/FALSE format
Notation
Interpretation:
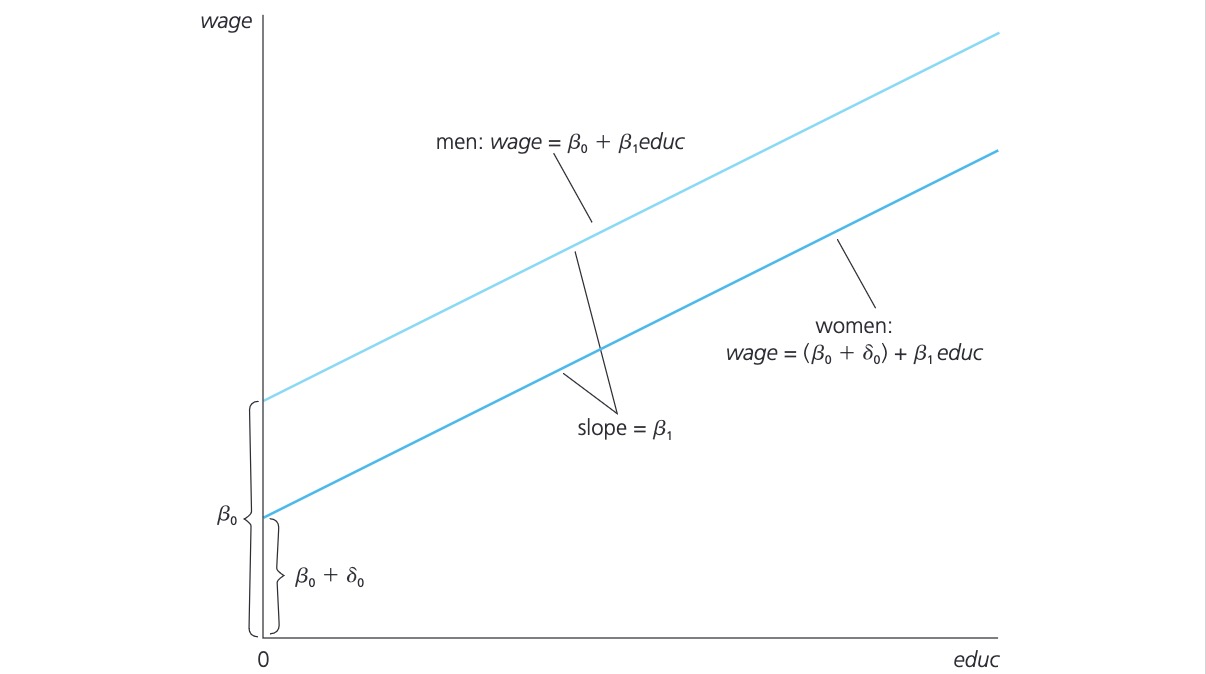
\(\delta_0\) = difference in wage between men and women (c.p)
\(\delta < 0\): women earn less
Representation:
Log Interpretation of Dummy Variables, e.g \(\ln wage = female + educ + exper\)
Roundabout: like a normal estimate: \(100 \cdot \delta\)
exact: \(100 \cdot [exp(\delta) - 1]\)
Dummies for multiple categories#
e.g. Model for wage differences across groups (married men, married women, single men, …)
create dummies for each (marrmale, marrfem, singfem)
base group = single males (have 0 and 0 on both categories)
Difference between single women and married women? Reestimate
Alternative: Interactions
e.g:
single men: female=0, married=0
married men: female=0, married=1 => \(.321+.213 = 0.534\)
Binary as dependent variable#
a.k.a linear probability model
Try to explain the binary outcome
e.g. college student using drugs in given school year
Example: Wome working outside home (labor force participation)
another yerar of education = increase probability by 0.038
10 years = 10(0.038) = 0.38
Note:
LPM is always heteroskedastic
caution with standard errors