10.01.2024 Tax Incidence#
Three rules#
Statutory burden \(\neq\) economic burden
side of the market = irrelevant
parties with inelastic supply = bear taxes
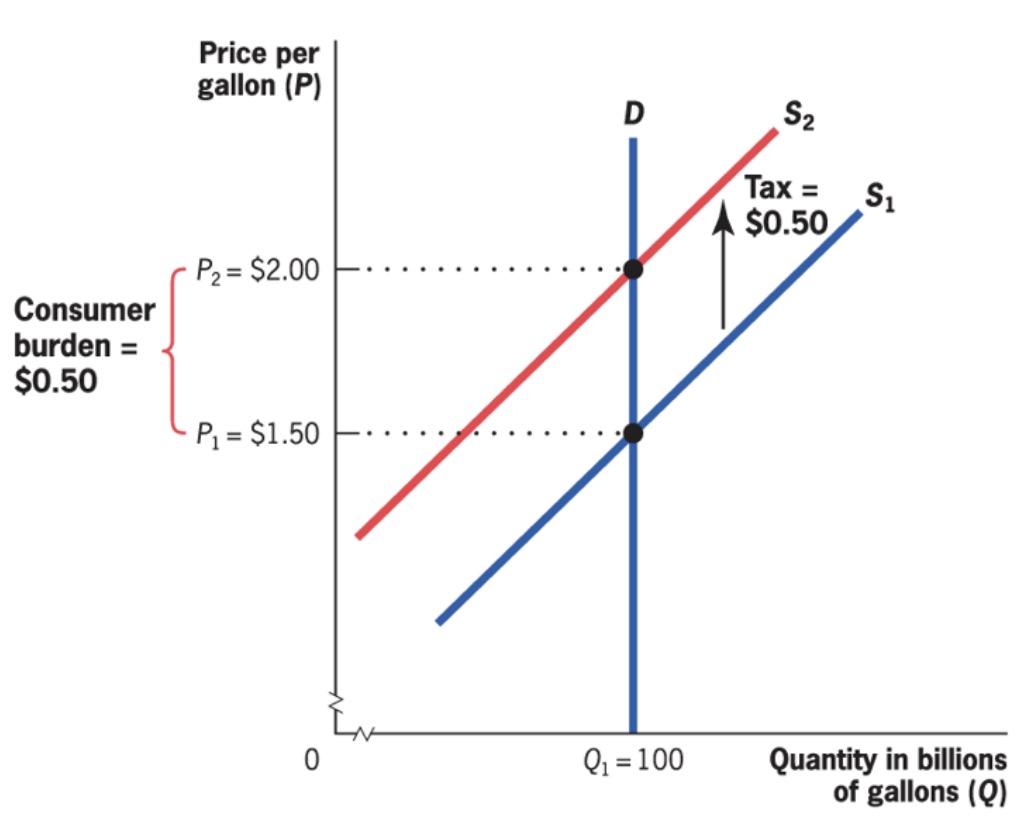
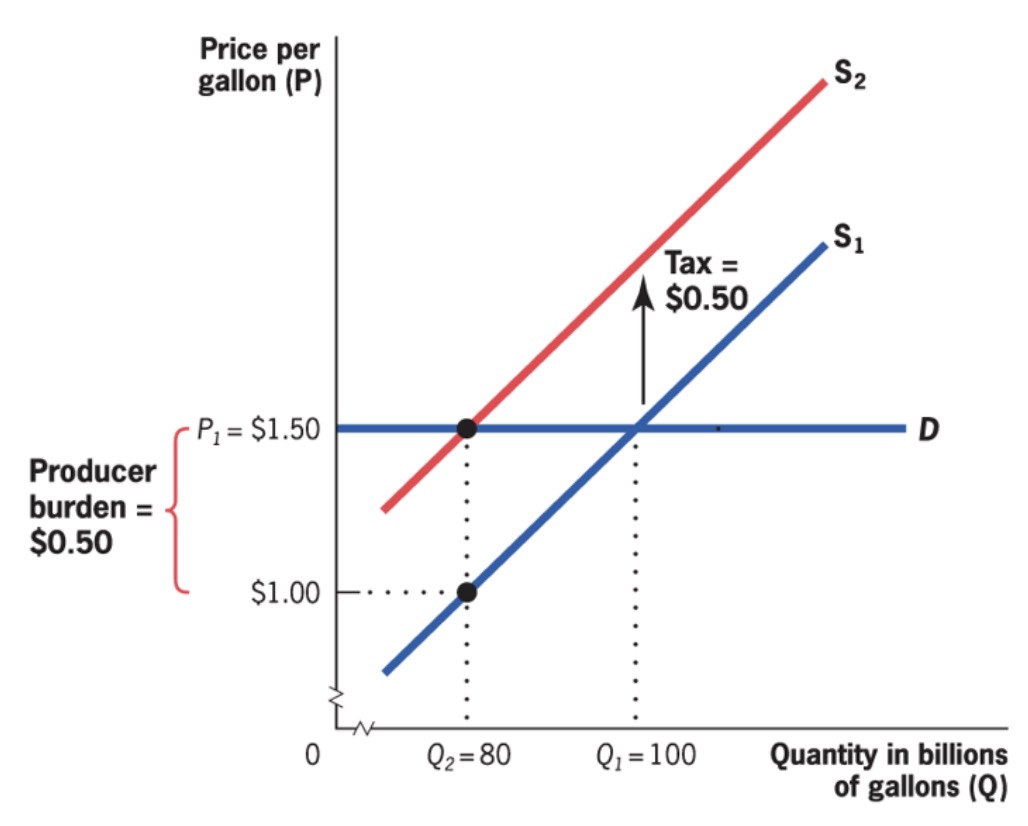
Statutory and economic incidence#
Economic Incidence: burden of taxation measured by change in resources available
statutory incidence: burden borne by party that sends check to gov.
Example:
Calculation for Consumers:
Producers vice versa
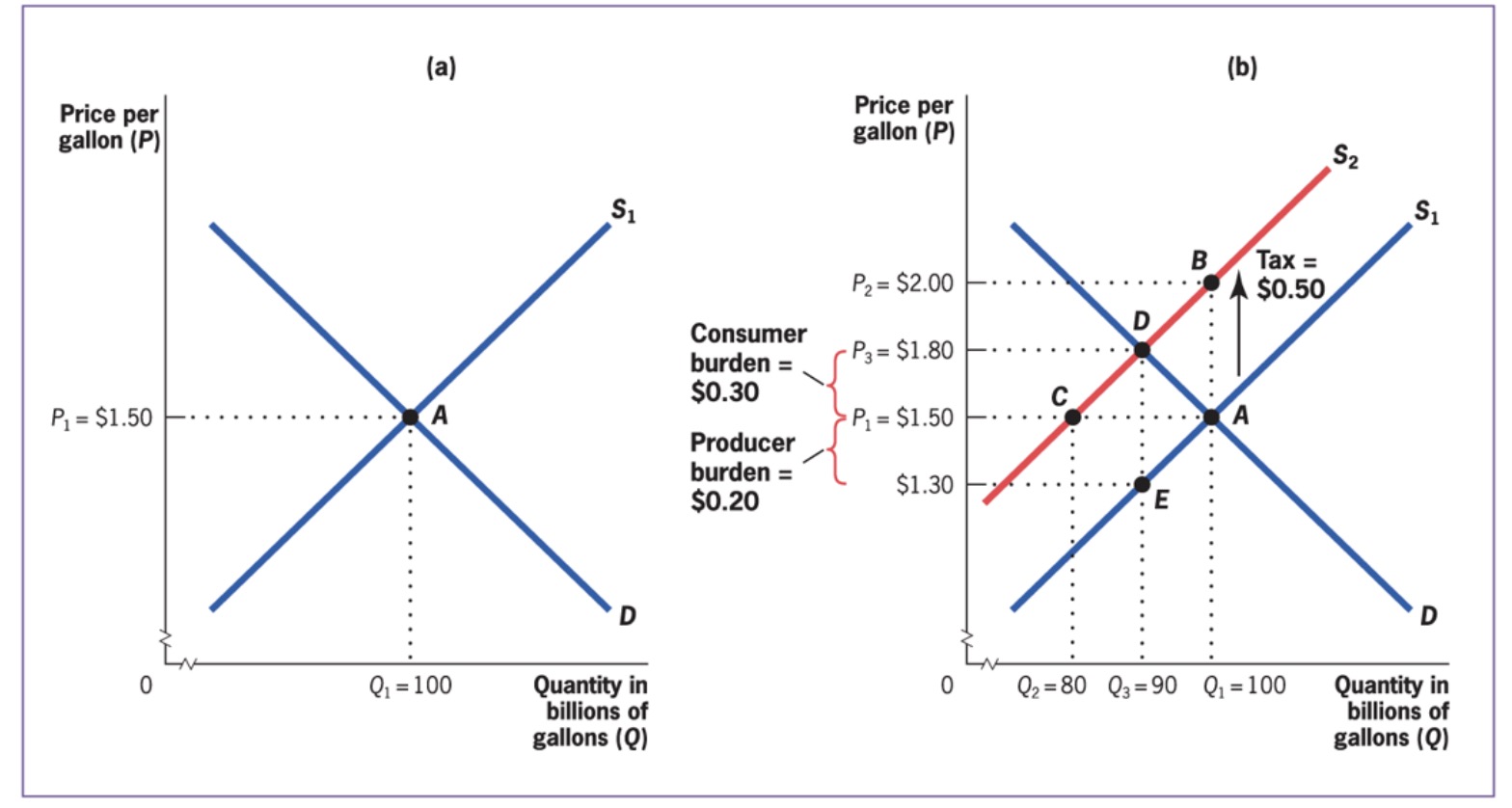
Tax Wedge: difference between consumers pay and producers receive
e.g consumers pay 1.8, producers receive 1.30 => wedge is 0.5 to government
Tax Side does not matter#
Exampel from before, but other side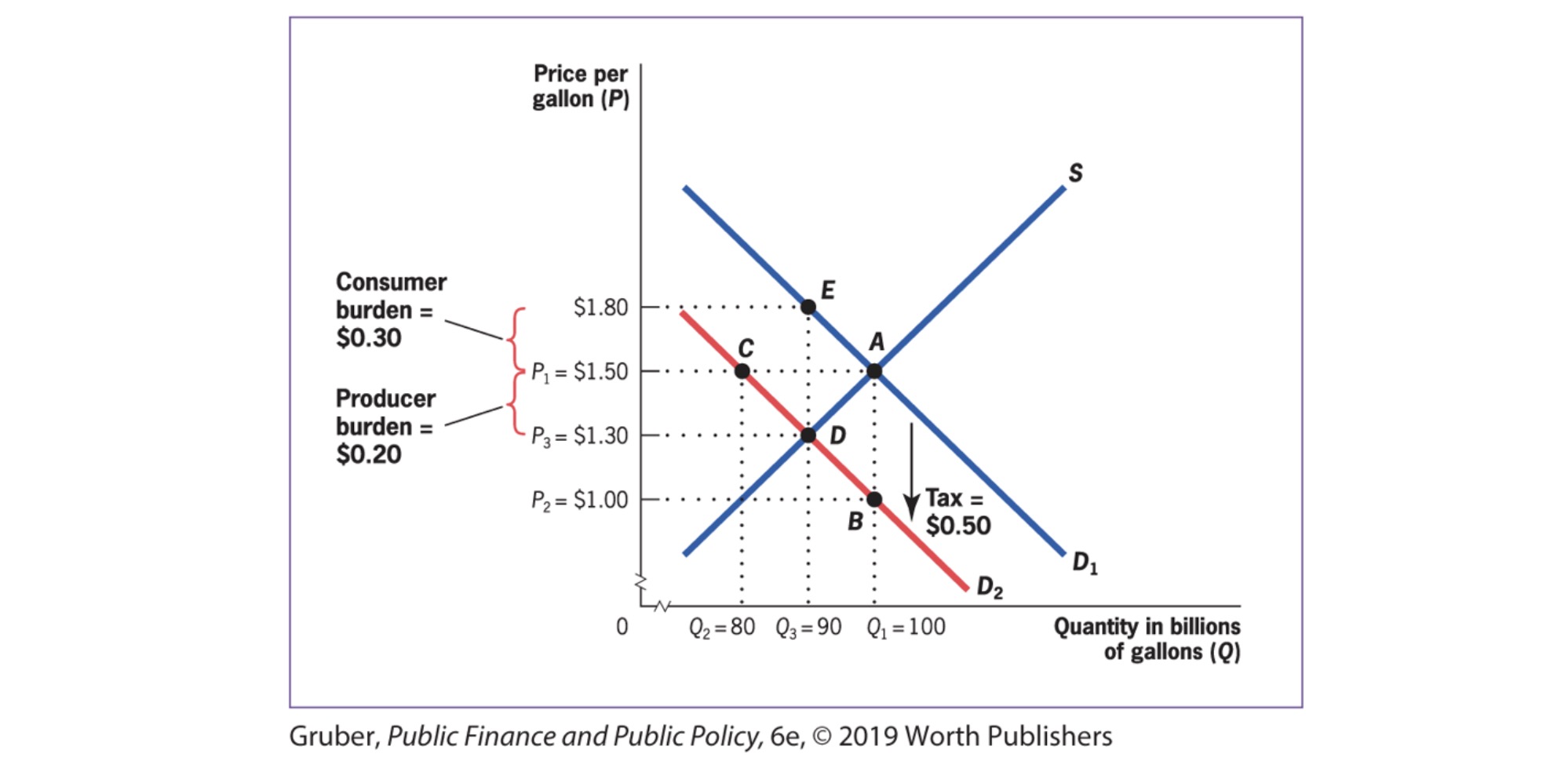
Gross Price: market price
After-Tax price: gross - tax
Elasticity#
inelastic demand |
elastic demand |
|---|---|
|
|
burden at consumers |
burden at producers |
Vice-versa for supply side
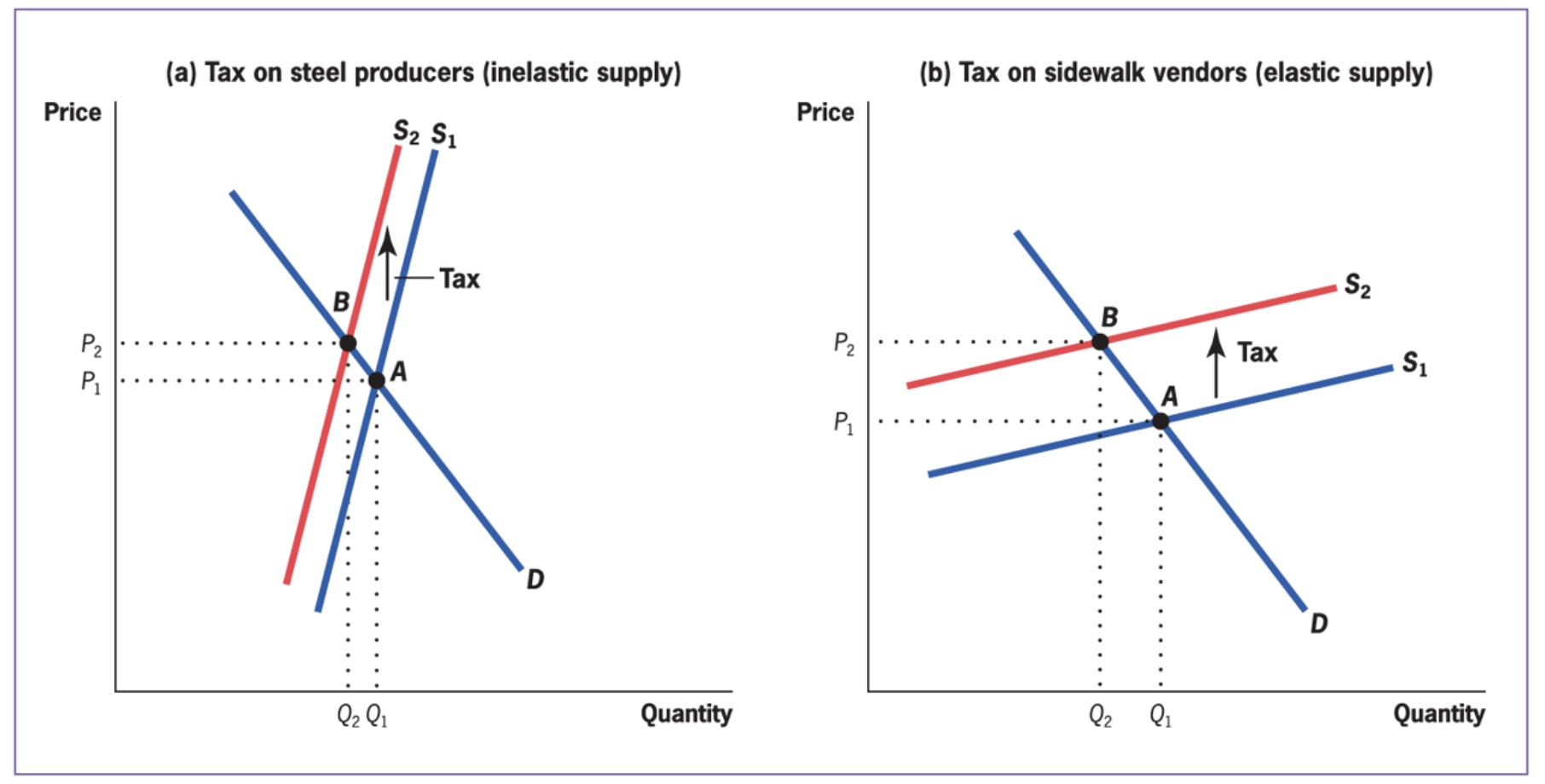
also applies for factor markets!
Balanced Budget Incidence#
Tax Incidence Analysis that accounts or tax & benefit
Hard to determine
analysis of tax benefits
General Equilibrium Tax Incidence#
partial Equilibrium tax incidence: tax effect on one market in isolation
general equilibrium tax incidence: tax effect on related markets
Vertically (within market)
horinzontally (across markets)
Issues:
elasticities differ in long / short run
spill over effects
easines to find untaxed subsitutes (tax scope)
Example: Tax on Restaurant
effects on other goods
Income Effect
Substitution Effect
Complementary Effect
e.g higher demand for movies as alternative time