05.07.2023 Instruments of Trade Policy#
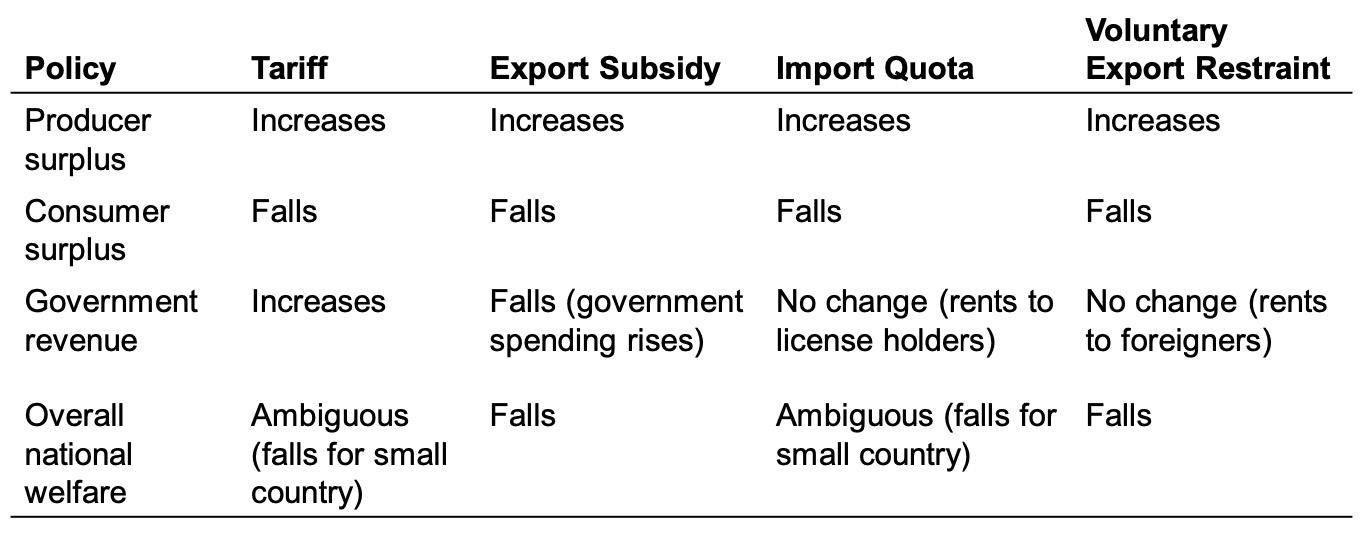
Summary of all options:
Tariffs#
Types:
specific tariff: per unit
ad valorem: as % of value
Situation in one-good and tariff:
Import Demand Curve#
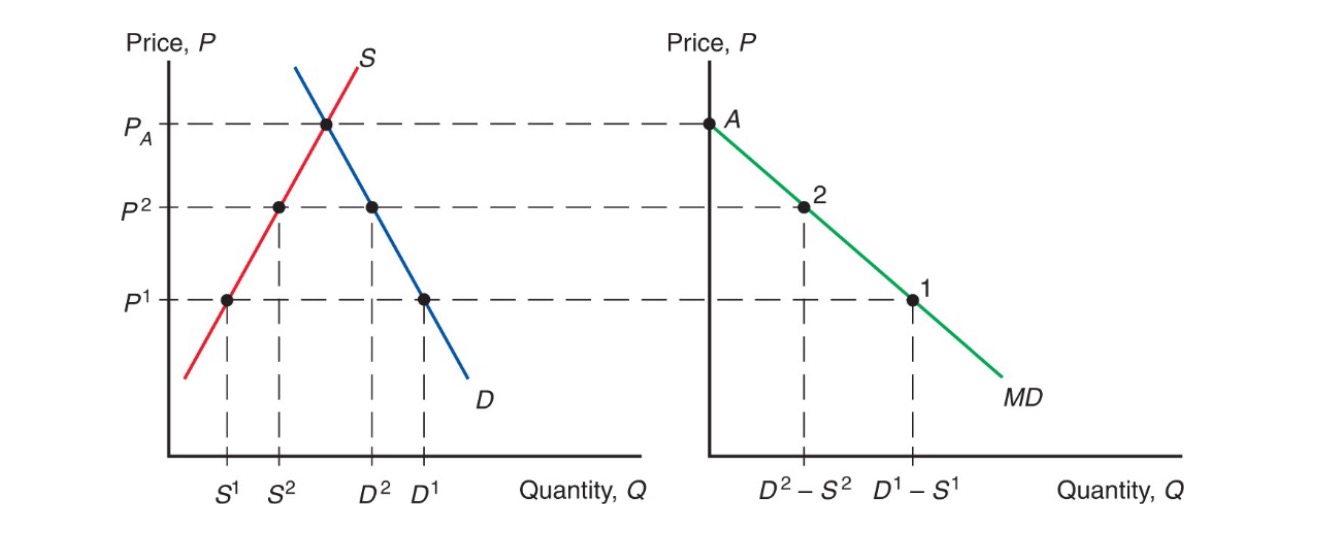
where foreign price less than home
\(MD = D-S\)
downward sloping (higher world price = less imports)
Export Supply Curve#
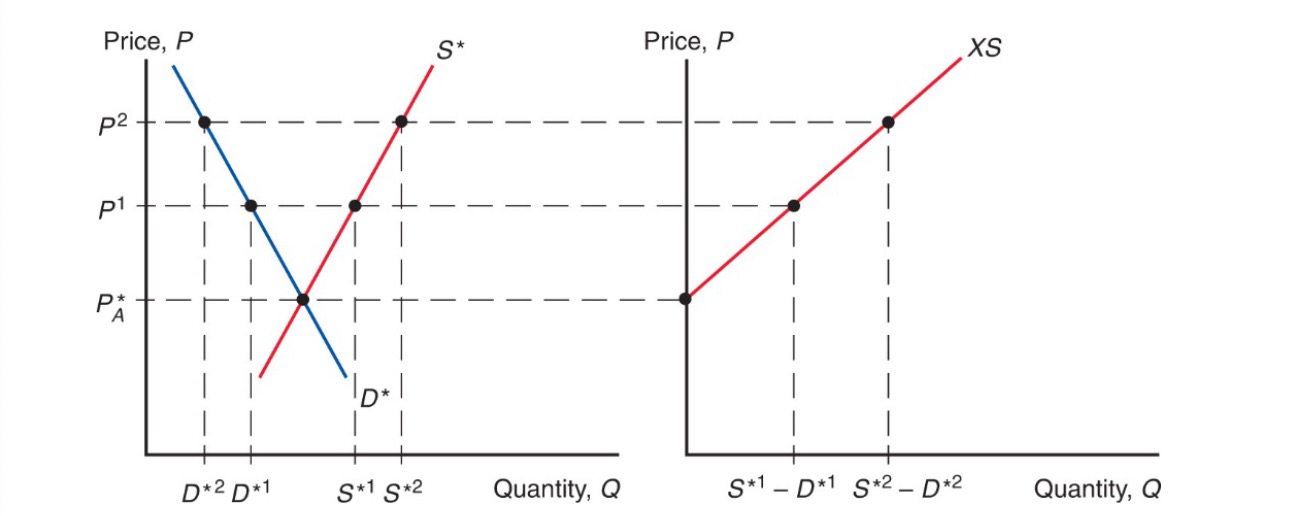
from perspective of foreign country
\(XS^* = S^*-D^*\)
upward sloping
Equilibrium: Import Demand = Export Supply
Effects of Tariff#
= Transportation Cost
unwilling to trade unless foreign price compensates tariff
\(P_t - t > P_t^*\)
higher price home, leser foreign
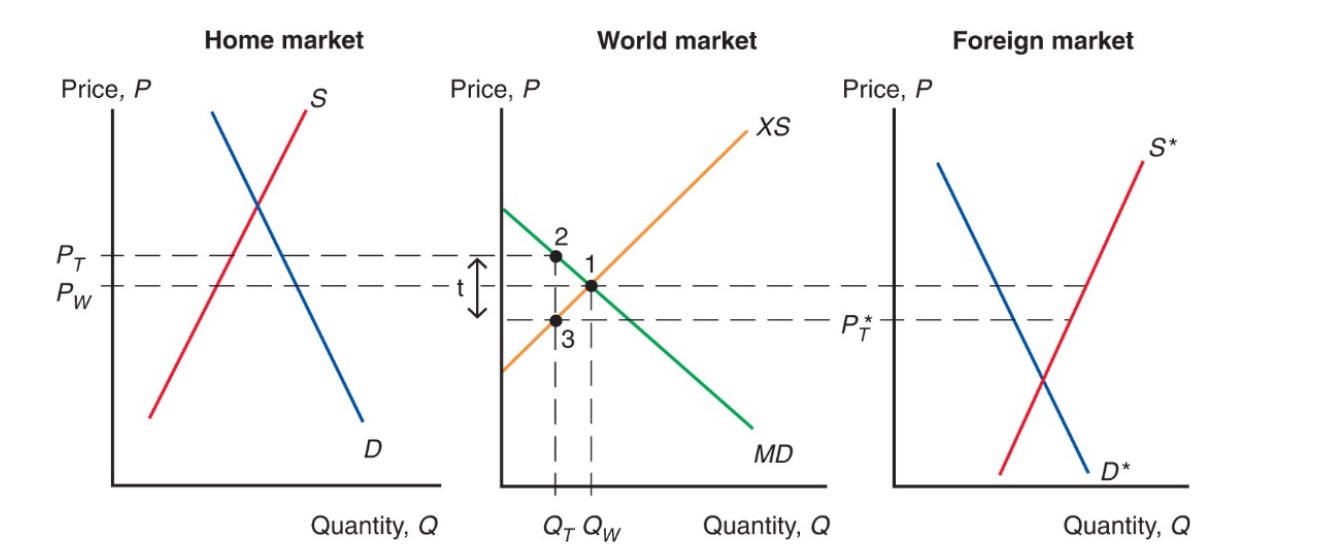
=> less traded, higher prices
tariff increase not completely on home price
of country small = no effect on world price = complete markup tariff
Amount of Protection#
effective rate of Protection: Change in value added for producers after trade policy change, depends on price change of good
Example:
before: 8000€ Cars with inputs 6000€ = 2000€ value added
After: 25% tariff increase
price now: 10000€ (8000*1,25) for car
factor prices same = 10000-6000 = 4000€ value added
rate of protection: \(\frac{ 4000-2000 }{2000}=100\%\)
Here: rate of protection > tariff rate
Cost and Benefits#
consumers = higher prices
producers = more profit
government = tariff money
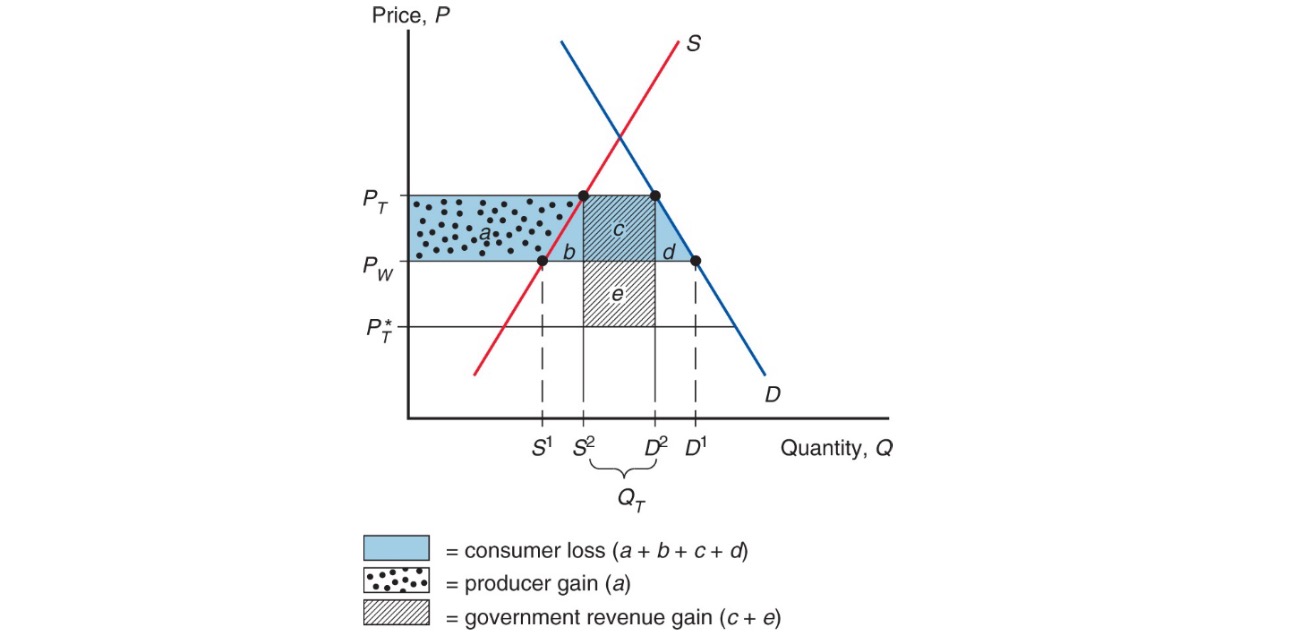
d+e = efficiency loss
e = terms of trade gain (lower foreign prices)
only possible for large countries
Problem: Retaliation and Wasteful activities
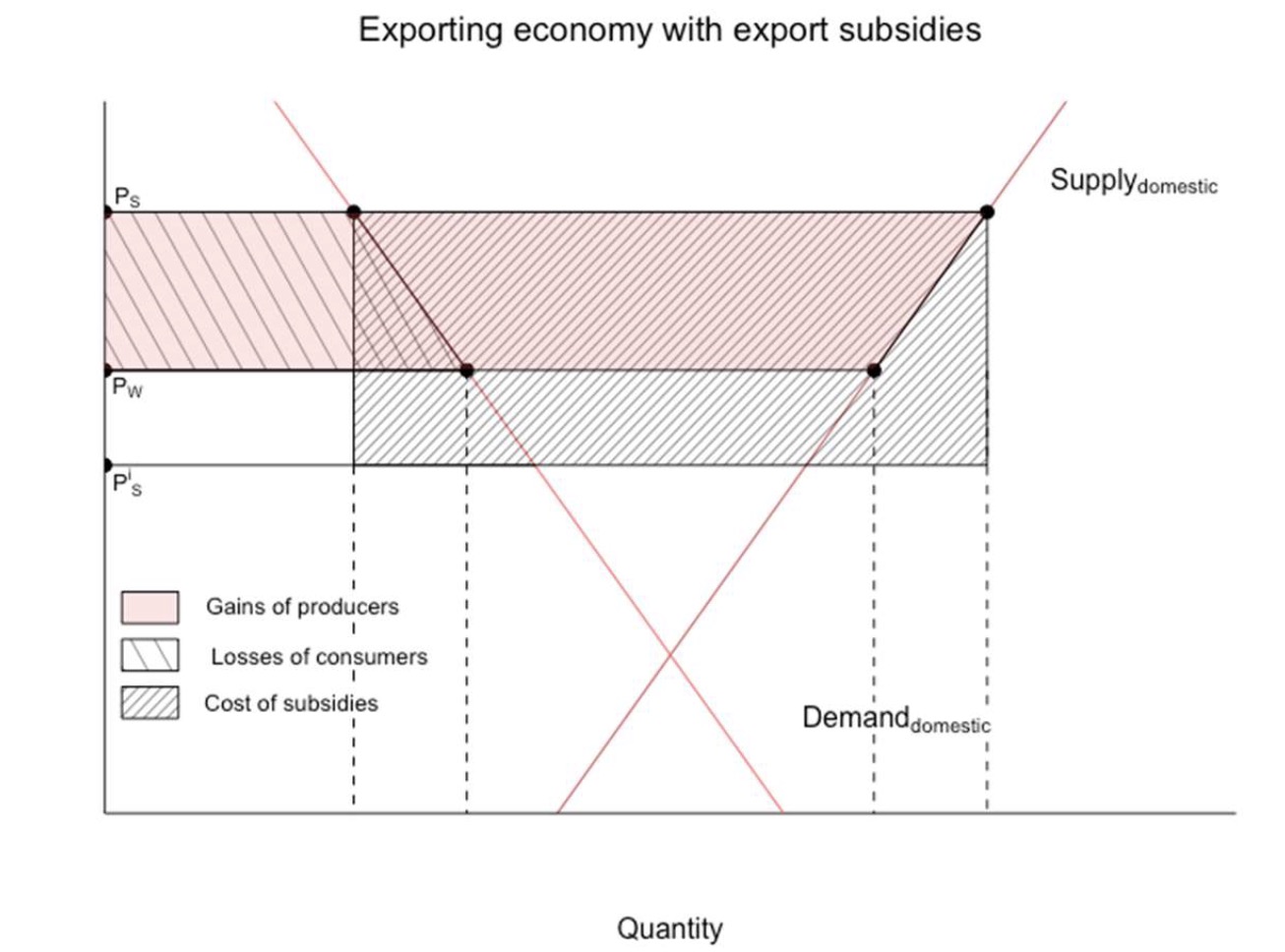
Export Subsidy#
Types: specific or ad valorem
less government revenue
lowers price in importing country: \(P^* = P_s-S\)
higher price for home consumers
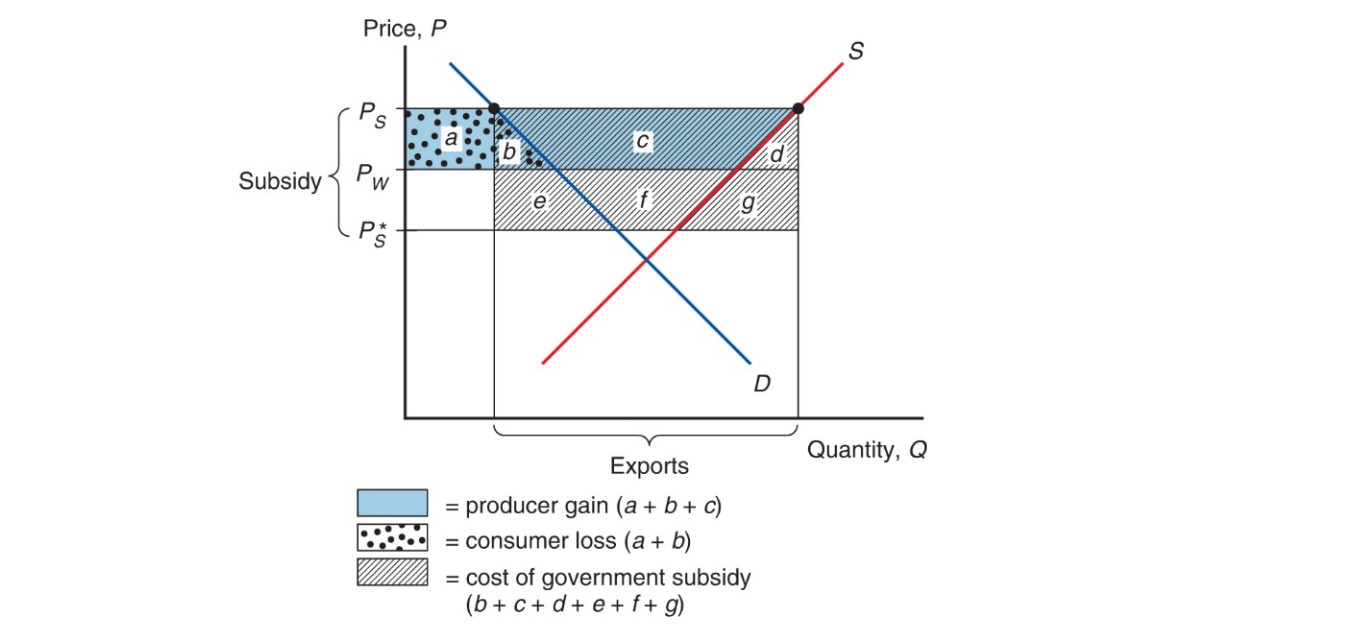
Import Quota#
Restriction of Quantity that may be imported
no government revenue
quota rents to license holders
rents to producers, cost to consumers
US Sugar Prices vs. World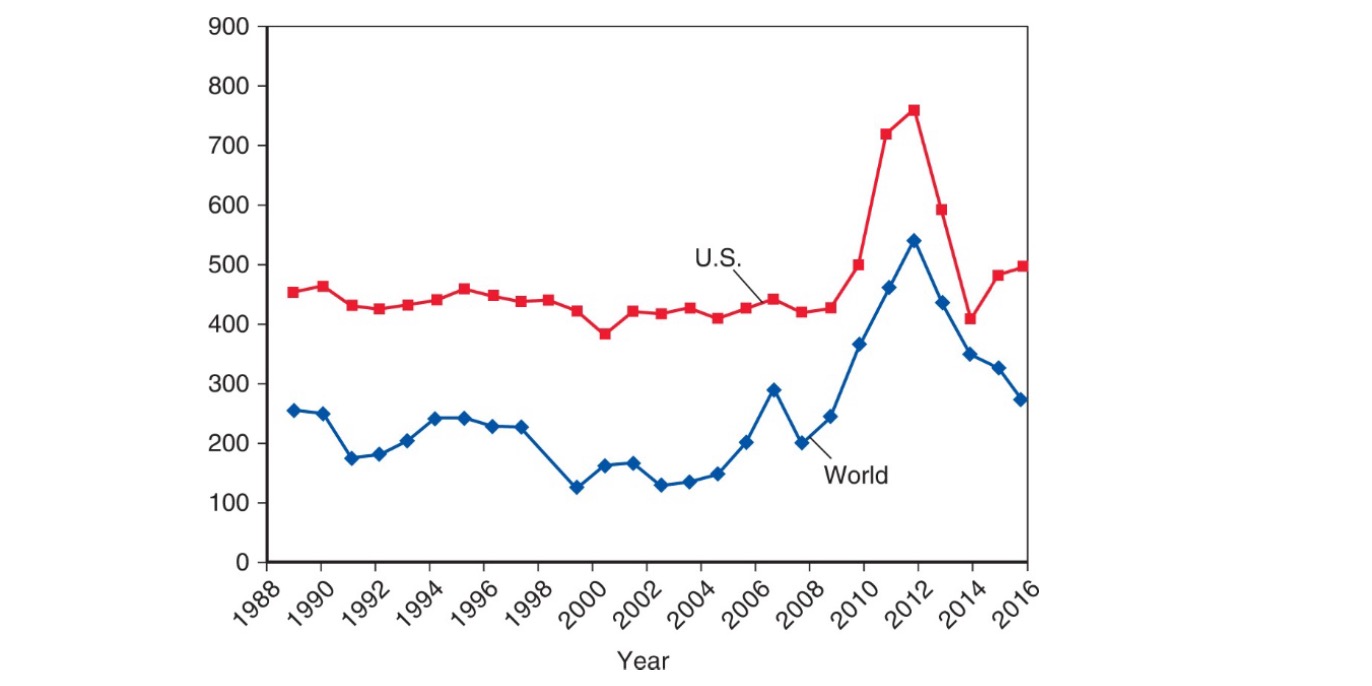
Voluntary Export Restraint#
Voluntary Export Restraint (VER): quota imposed by exporting country on its exporting industry
due to pressure by Importing Country
Example: Japanese Cars in US Market
Price rose of japanese fuel efficient cars
rent to japanese firms
Local Content Requirement#
Local Content Requirement: regulation, that fraction of end product domestically produced
either value terms of unit terms
no revenues
home producers of inputs like import quota
home producers of outputs not as strict
price diff average between no quota and import quota
Exercise#
Free Trade Situation#
Country A $\( \begin{aligned} D &= 100-20P \\ S &= 20+20P \\ MD &= D - S = 80-40P \end{aligned} \)\( Country B \)\( D = 80-20P \\ S = 40+20P \\ XS = S-D = -40+40P \)\( Equilibrium \)\( 80-40P = -40+40P \\ \to P = 1.5 \ , Q_{trade} = 20 \)$
Tariff#
Tariff inhome country: \(t=0.5\) $\( MD = 80-40 (P+t) \\ XS = -40 + 40P \)$ Equilbirum:
Import Demand to the Left
less Imports / Exports from other country
higher price
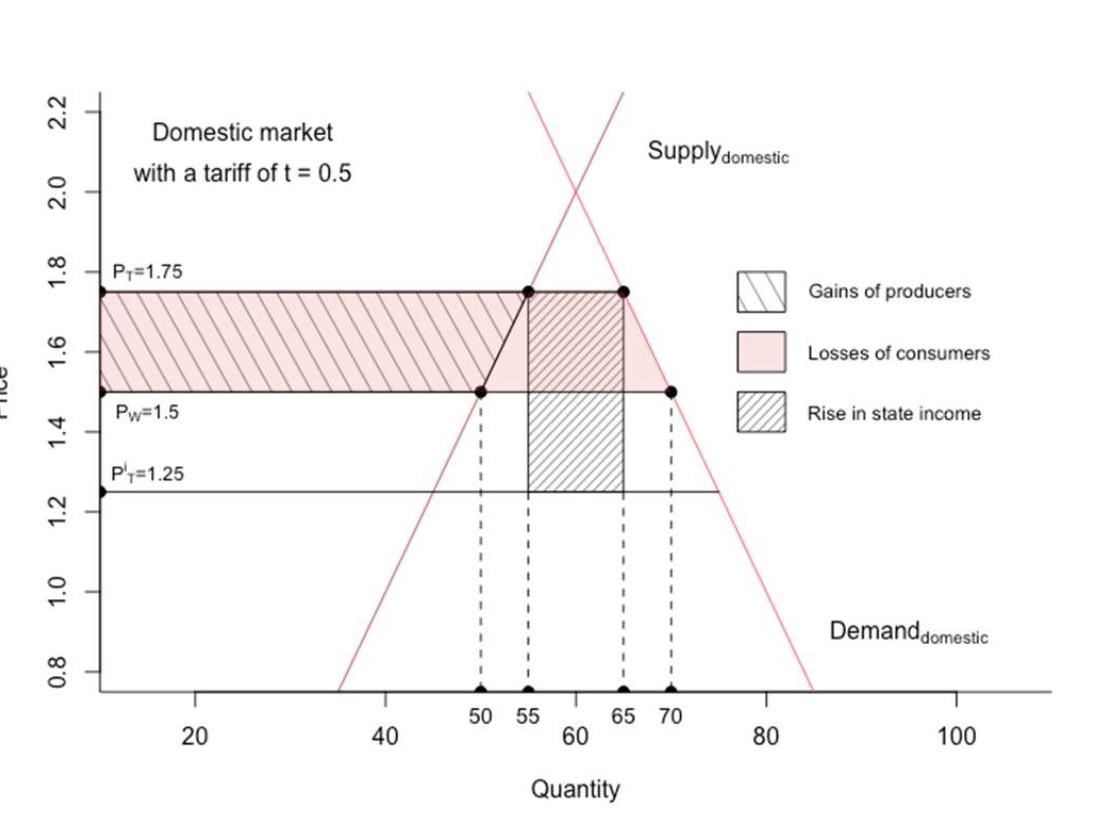
world market price: 1.25 + tax = 1.75 home price
=> tariffs leads to sinking world prices, cancels out some of the tariff
Tariff with big country#
Equilibrium without Tariff $\( 80-40P = -400+400P \\ 480 = 440P \\ \to P=1.0909, Q= 36,36 \)\( with Tariff \)\( 80-40(P+t) = -400+400P \\ 480 = 400P+40P+20 \\ 460 = 440P \\ \to P_{world}=1.045, Q=18,2 \)\( Price with tariff: \)P_{tariff} = 1.545$
=> small country shoulders most of the price increase!
Effective Tariff = nicht klausurrelevant
Surplus#
with original Situation
with small country
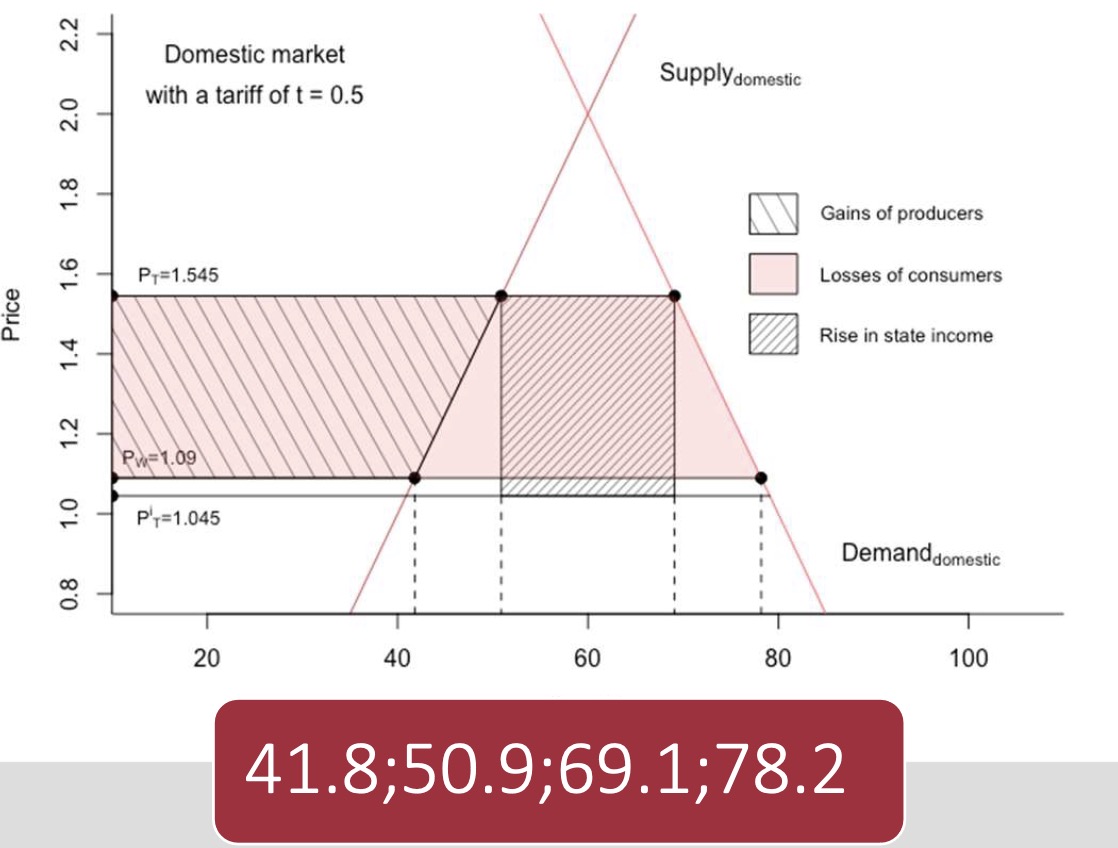
\(P_t-P_w=1.545-1.09=0,455\)
Zwischending = 9,1
Triangle: \(0.455*9.1 = 4,1405\)
Surpluses:
Government: \(0.5*(69.1-50.9)\)
Producer: \(41,8*0,455+4,1405\)
Consumer: \(69,1*0,455\)
Export Subsidy#
new Sitatuion
$\(
MD = 80-40P \\
XS = -40+40(1+0,5)P
\)\(
Equilibrium
\)\(
80-40P = -40+60P \\
P_{import} = 1.2, Q=32\\
P_{export} = 1.8
\)$