13.04.2023 The Firm#
Firm: a business organization
employs people
inputs to outputs
price > cost of production
concentration of power in owners / managers
Structure#
separation of ownership (shareholders) and control (managers)
a principal Agent Problem
inner firm is different to markets:
market = voluntarily,
Work = involuntarily
firms are structured around contracts, without price mechanism
Contract#
Contract: legal understanding, that specifies a set of actions that parties must undertake
transfer of authority, not ownership!
in wage relations = incomplete
do not specify every aspect
not always perfectly enforceable
firms do not force employess to stay on job
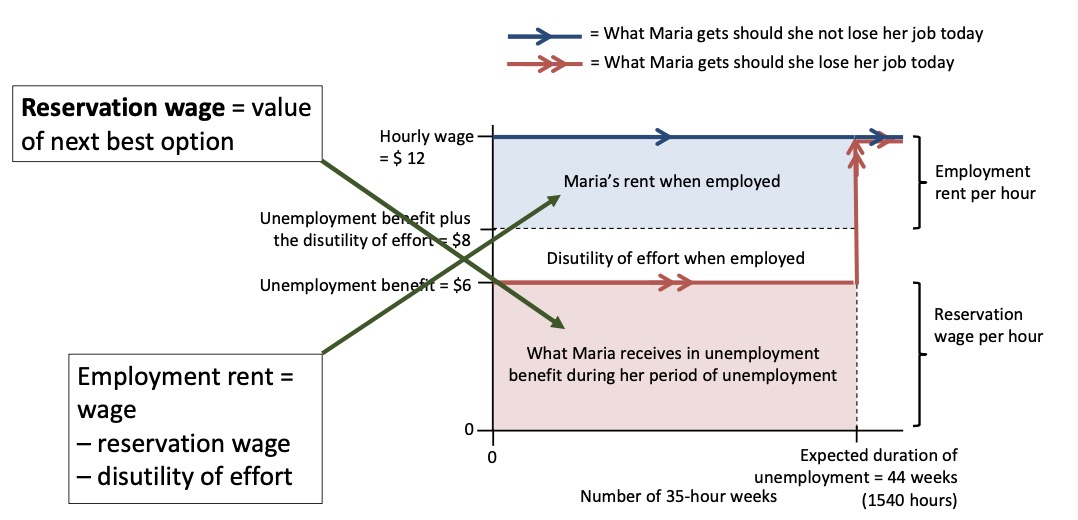
Employment rent#
how to compensate workers? with wage!
employment rent > reservation wage (alternative)
cost of job loss
induce workers to stay on job
also includes calculation regarding unemployment benefit
Labor Discipline#
why do high wages motivate us?
higher wage
higher employment rent
higher cost of job loss
more motivation
=> workers choose effort based on wage!
Workers best response curve to wage offer
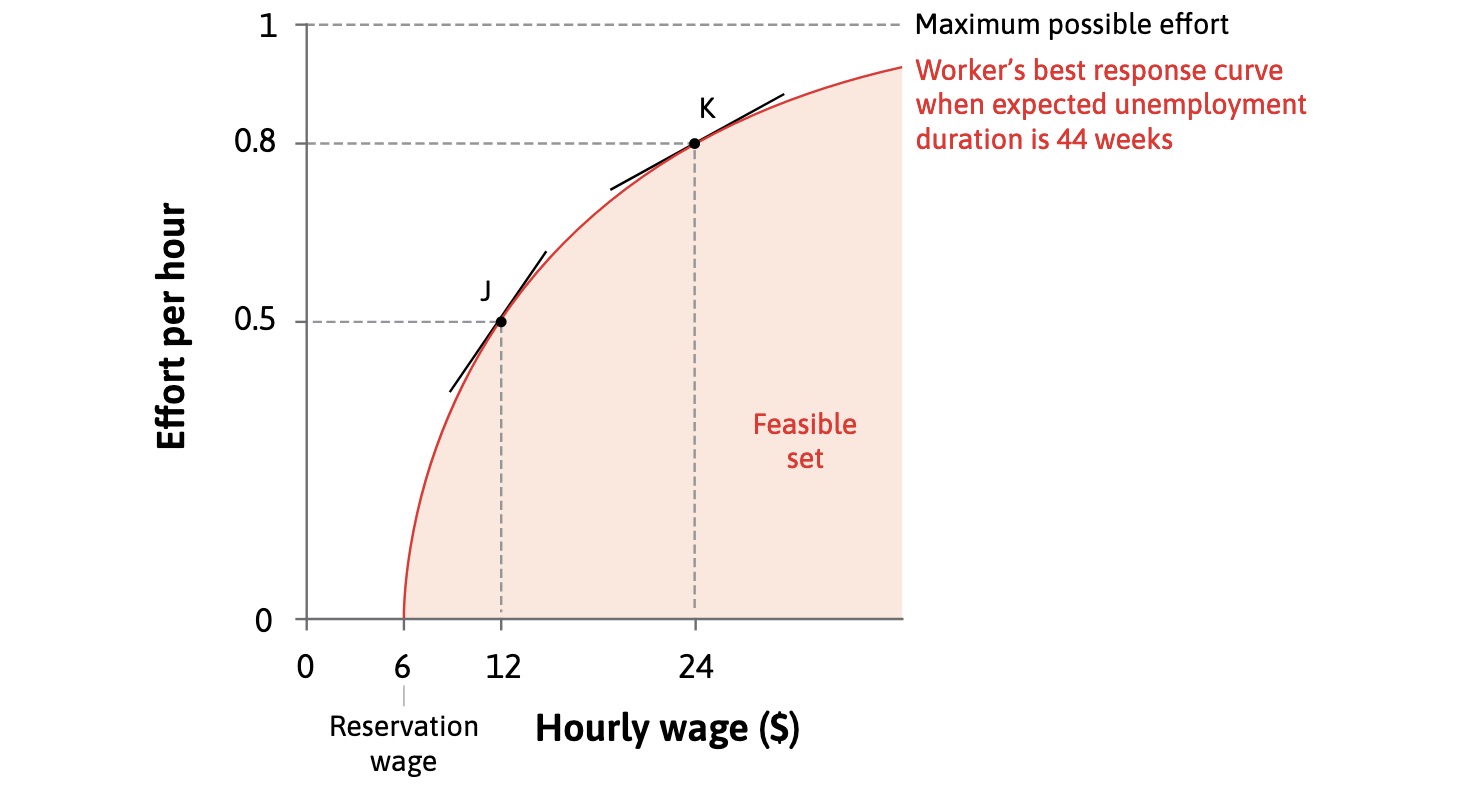
Workers Best Response Function: $\( e = E(\underset{+}{w},\underset{-}{a}, \underset{+}{p},\underset{-}{b}, \underset{+}{d}) \)$
e = effort Level
w = wage
a = disutility of effort
p = probability of getting fired
b = unemplyment benefits
d = duration fo unemployment
Profit#
firms maximize profit $\( profit = \underbrace{R(N \times e)}_{Revenue} - \underbrace{N\times w}_{Costs} \\ \implies profit = R(N*w*\frac{e}{w})- (N*w) \)$ the higher the effort per wage dollar, the higher the profit
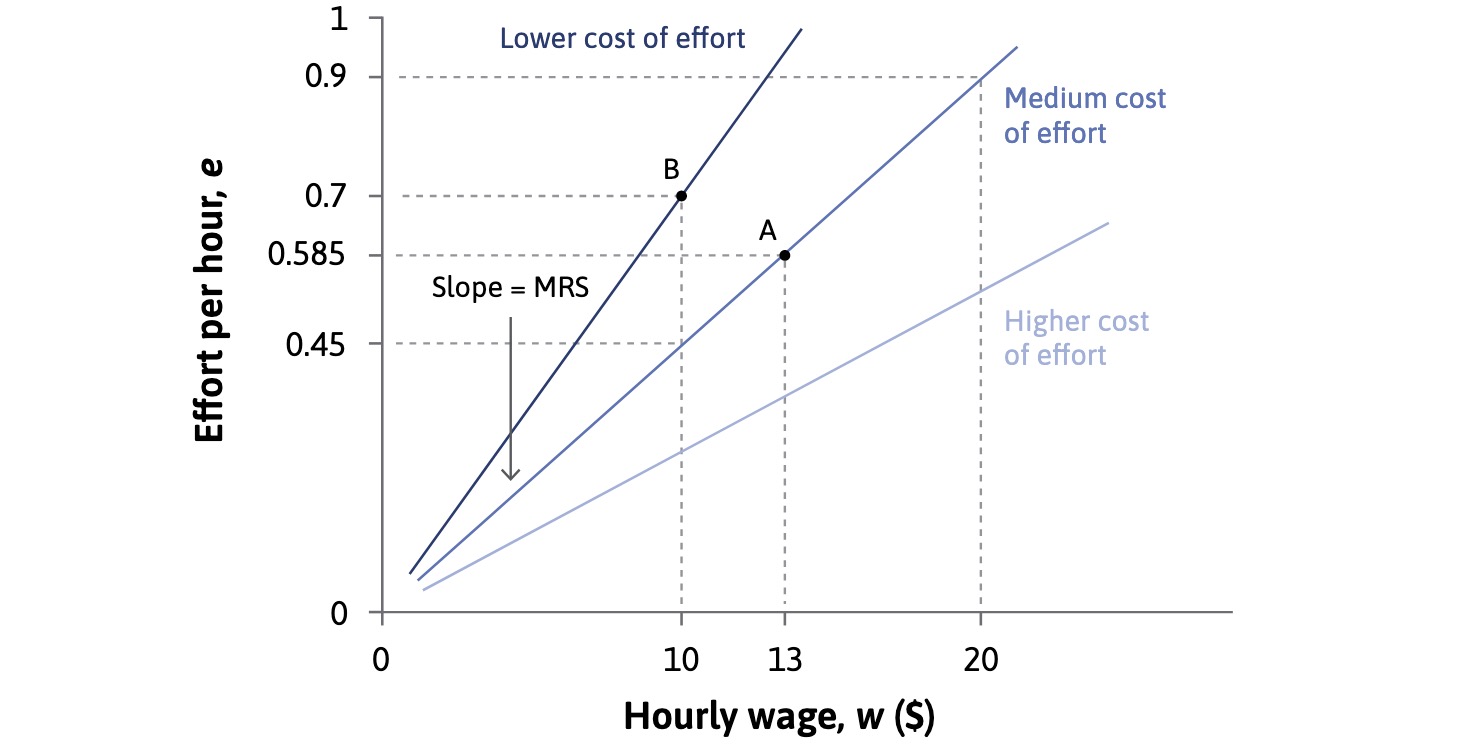
Wage#
gets determined at MRS = MRT
but shift at policy shocks:
higher benefits = less effort
higher unemployment = more effort
higher wages can be profitable for firm (adverse selection, turnover, …)