04.05.2023 Banks III#
last Lecture: Credit Market Failures
Wealth and Credit#
Decisions by the Banks and Lenders
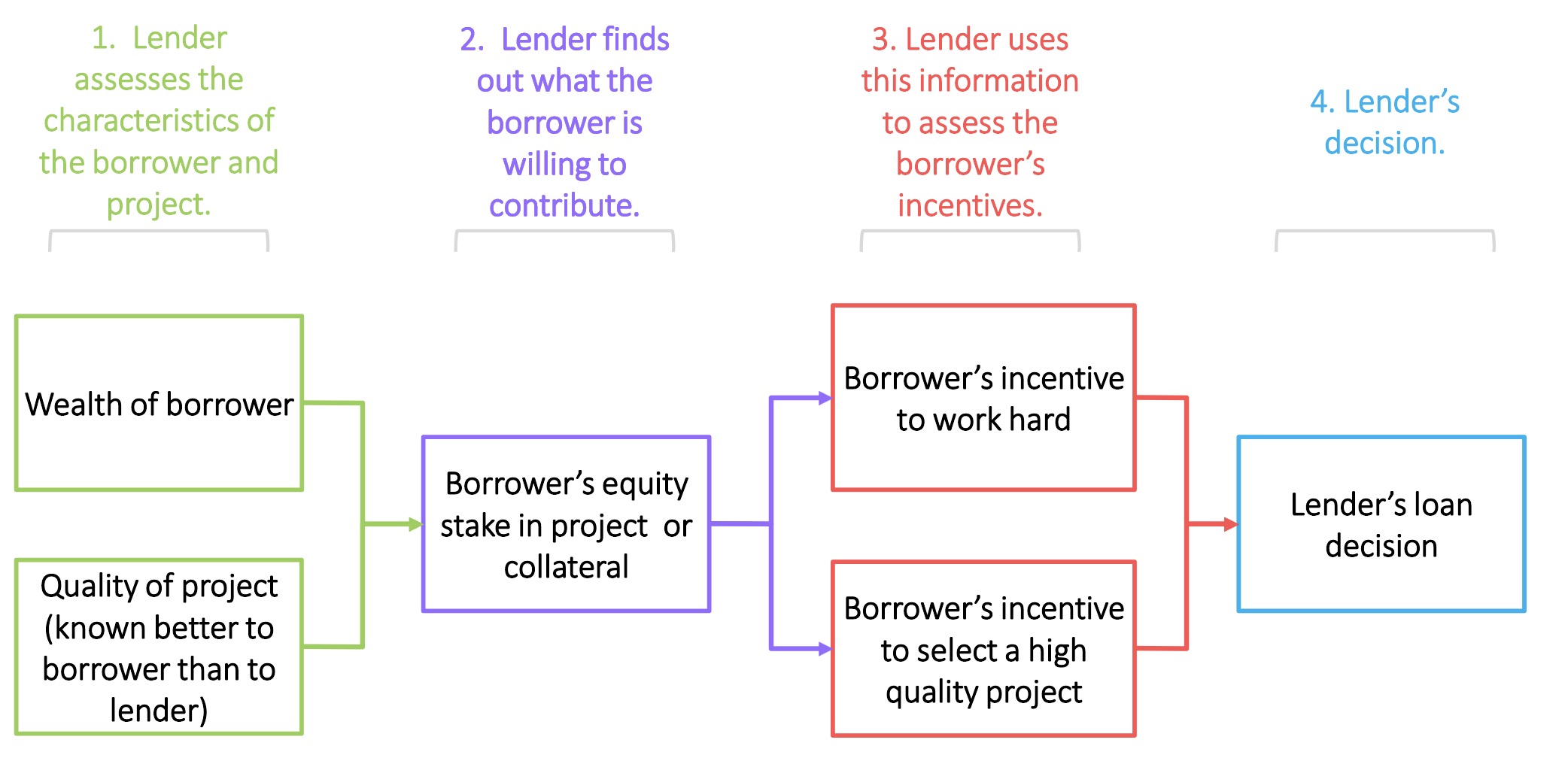
Contributions by Lender
Collateral (Sicherheit)
equity (Eigenkapital)
reduces Risk for Bank => higher lending
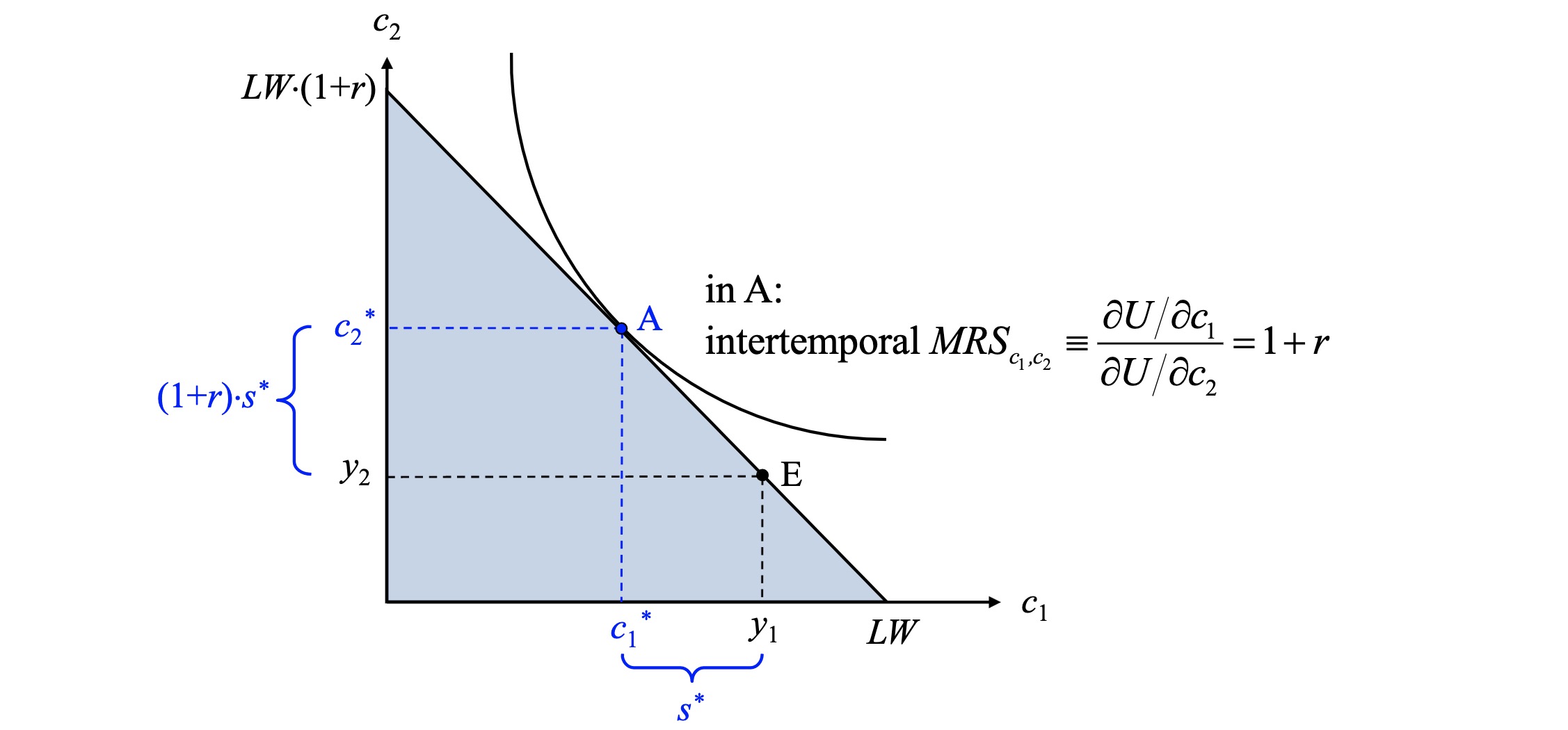
2 Period Model#
\(y_1\) and \(y_2\) (income now and then)
\(c_1, c_2\) (consumption)
saving possible today
interest rate r
Constraint#
Consumption Possibilities $\( c_1 + s = y_1 \\ c_2 = y_2 + (1+r)s \\ \implies s = \frac{y_2-y_2}{1+r} \\ \)\( Lifetime budget constraint (LBC) \)\( \underbrace{c_1 + \frac{y_2-y_2}{1+r}}_{\text{present value of consumption}} = \underbrace{y_1+ \frac{y_2}{1+r}}_{\text{present value of income}} \)$
Preferences#
Consumer Preferences: \(U(c_1, c_2)\)
consumption smoothing advised
maximization
Equilibrium#
Example (Saver):
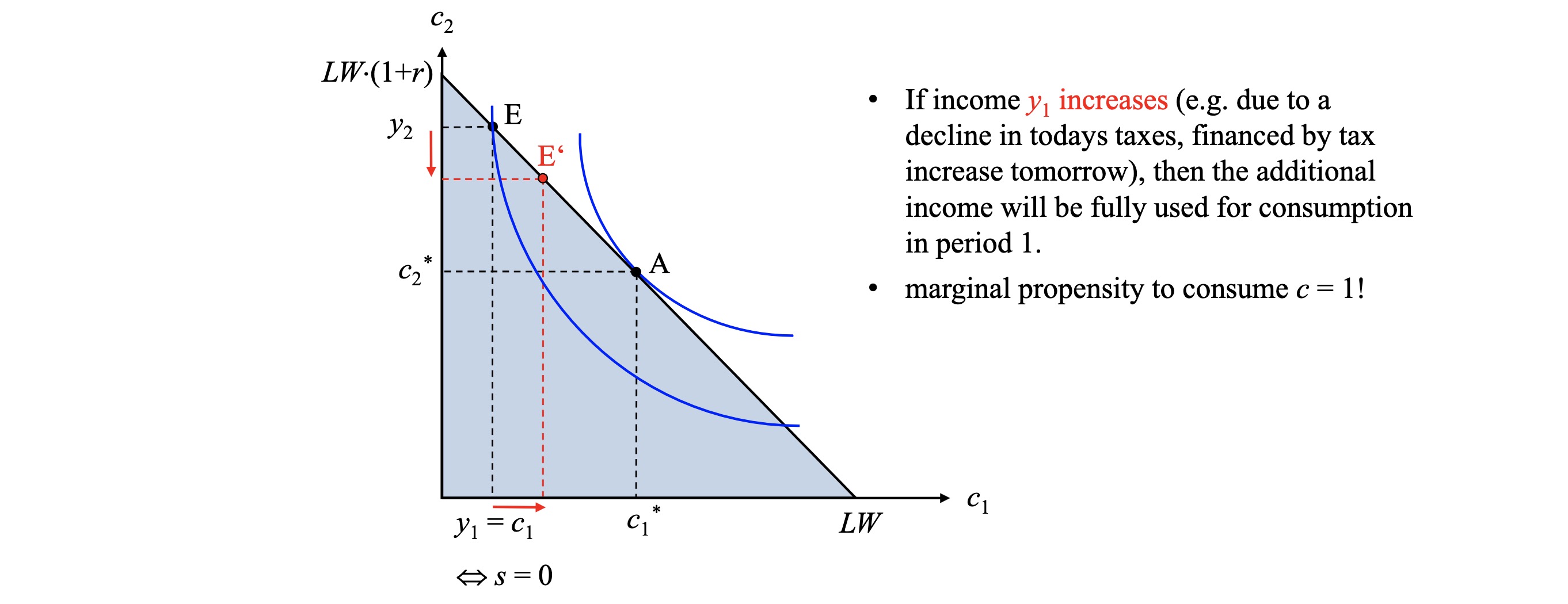
Problem: Credit-rationed borrowers (borrow limit)
not able to perfectly smooth from future to present
every possibility to borrow is used
every extra income is consumed today
=> marginal propensity to consume \(c=1\)
Roles of Banks#
Goal: maturity transformation: short-run to long run
Problem: Liquidity Risk
fractional reserves not enough for customers demand
panic -> bank run
Solution: Lender of Last Resort (LOLR)
Objectives of LOLR:
interdependence in banking sector (uncertainty spreads)
negative spillover effect
avoid moral hazard (Too big to fail)
Lending and Inequality#
inly some people are able to prfit by lending
credit rationing do not profit from borrowing