20.12.2023 Taxation#
Ways of Government Revenue:
Taxation
Debt
Fees / Contributions (Sozialabgaben)
Sales of Government Assets
General#
Tax (Legal): Cash Payment to State from everyone
Tax (Economic): compulsory levy without specific service in return
Economic = more broad, also non-financial e.g jury duty
German Taxes#
Earnings (Lohnsteuer)
Income (Einkommensteuer)
Individual income tax
capital gains tax
Corporate Income (Körperschaftssteuer)
Wealth
Wealth Taxes (sadly do not exist currently)
Property taxes (Grundsteuer)
Estate taxes (Erbschaftsteuern)
Consumption
Sales Tax (Mehrwertsteuer)
Excise tax (Zigaretten, Alkohol, …)
Assignemt to Budgets of
Federal: excise taxes
State: grunderwerbsteuer
Local: grundsteuer
divided: Einkommensteuer (Gemeinschaftsteuer)
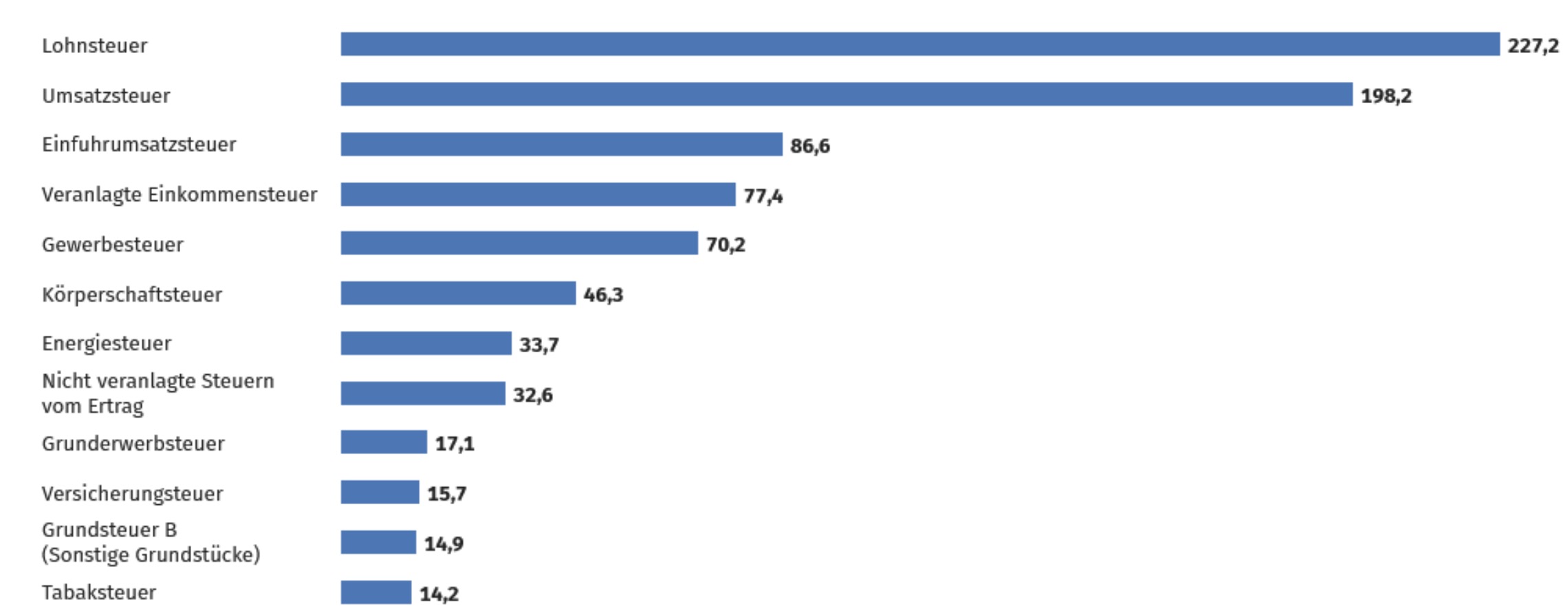
Revenues#
of different Taxes
Effective Tax Rates on Income
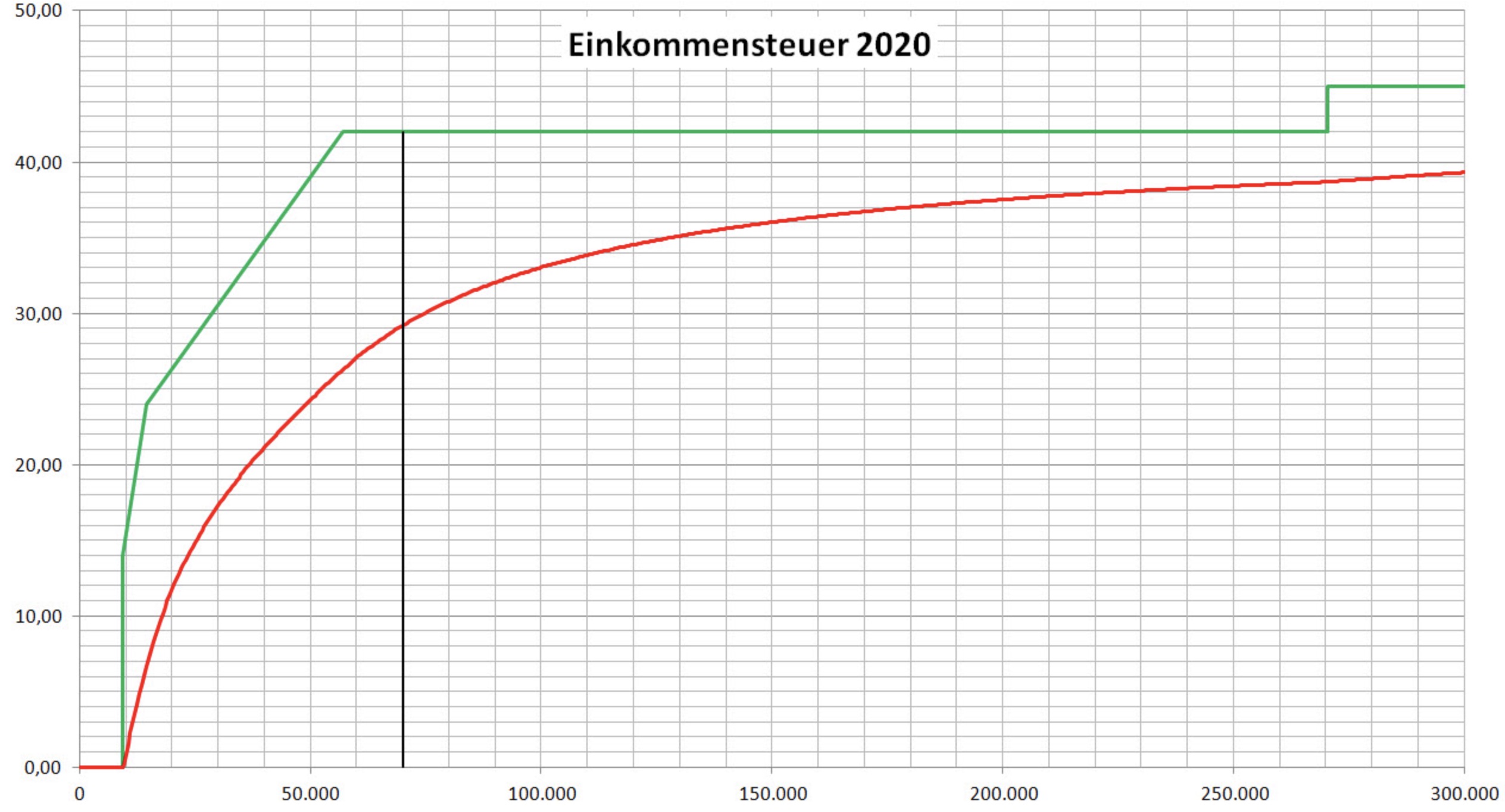
Red = effective Tax, green = marginal tax
marginal tax rate: percentage of the next euro of taxable income paid
effective tax rate: percentage of total income paid
Fairness#
Principles:
Vertical equity: higher income = higher taxes
Horizontal equity: similar people = similar taxes
Tax Base#
what income should be taxed? (Exemptions etc.)
Haig-Simons: focus on individuals ability to pay
assess monetary gains of perks (e.g company cars)
leads to higher equity
Measurement
Total consumption + Wealth Increases
deduct
business expenses
undesired consumption (e.g medical expenses)
Exception: Reducing Taxes on Activities with external Benefits
charitable giving
housing expenditure
Reasons for charity deduction:
Crowd In of additional money (marginal effect)
but lower gov. Spending (inframarginal impact)
empirical: some crowd in
consumer sovereignty
But: most people do not reasearch
gifts without benefit to targe
Housing Subsidy
for positive externality (does not exist)
no more houses bought
just for rich people
Unit of Taxation#
Household Members / Individual / Spoues
German example: Ehegattensplitting
Add up Incomes of both Spouses
divide by 2 => then add exemptions etc
leads to:
marriagy subsidy
lower incentives for work (for low earner)
distort decisions
ignores children
other countries:
Individual (19 OECD Countries)
Family Splitting with number of kids (US, Norway, …)
like Germany = Luxembourg