15.06.2023 Standard Trade Model#
General#
general Model, combines Ricardian, Specific Factors and Heckscher
two goods
each country PFF
Differences between countries:
labor
capital
technology
Countrys Decisions:
Production based on \(\frac{ P_C }{P_F}\)
to maximise value \(V = P_C Q_C+P_V Q_V\)
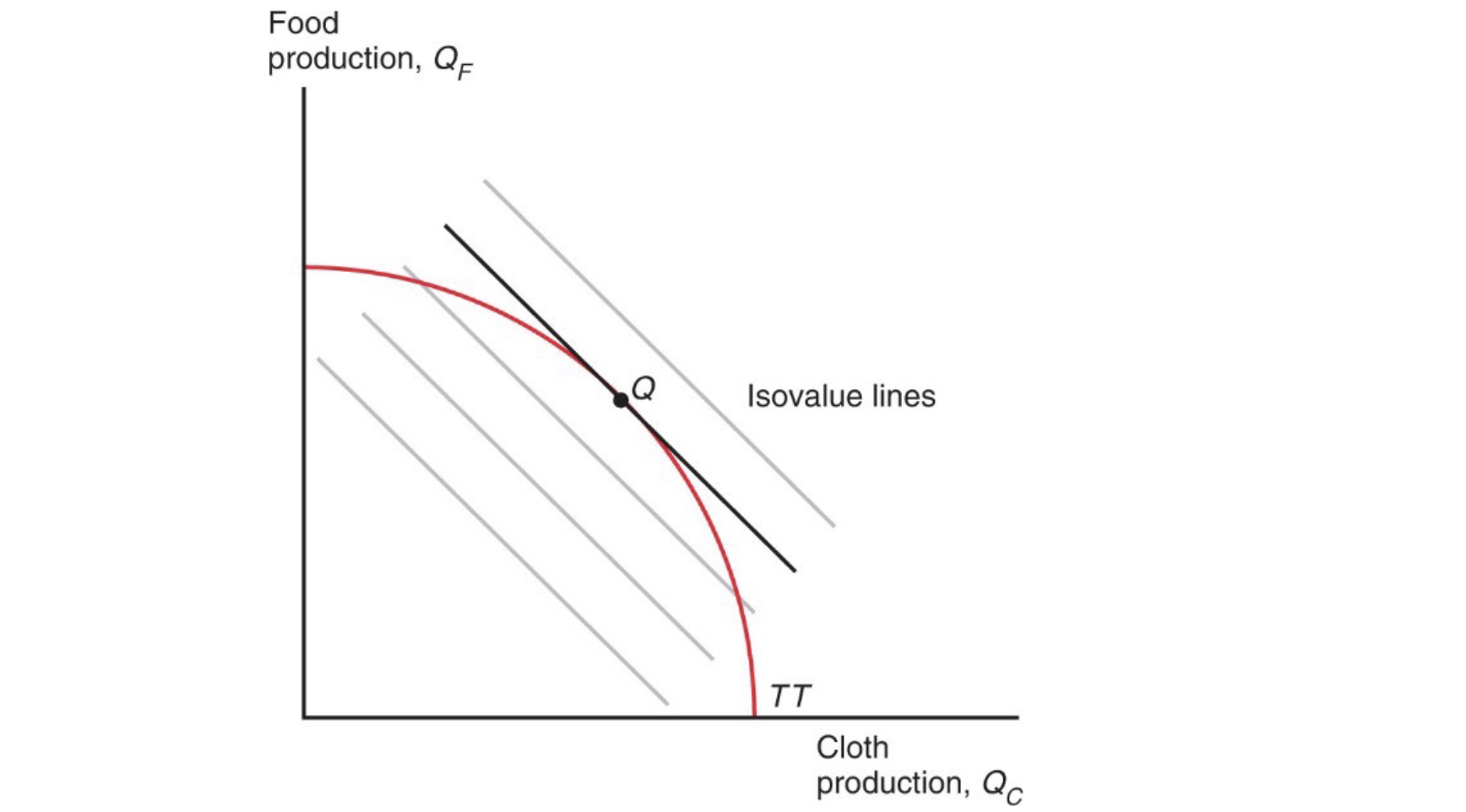
relative Price Increases => steeper Isovalue Line => other combination better
Relative Prices#
Demand equal to Supply
Assumption: single representative consumer with indifference curve
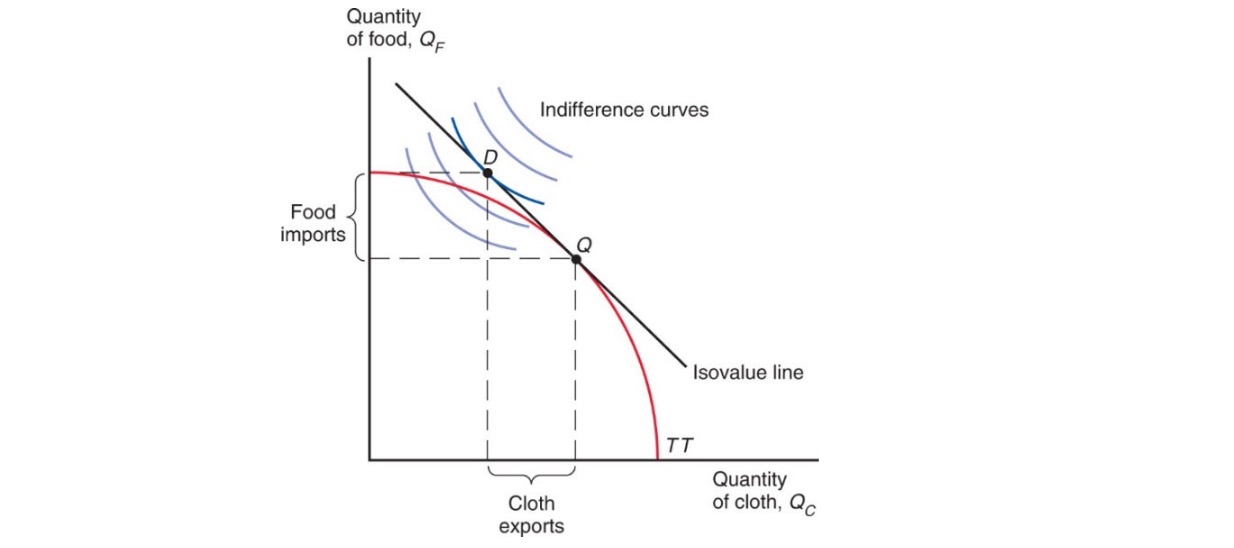
resulting Diagram with IDC and trade
Whole-Economy:
better off when export good relative price rises
More Imports per export
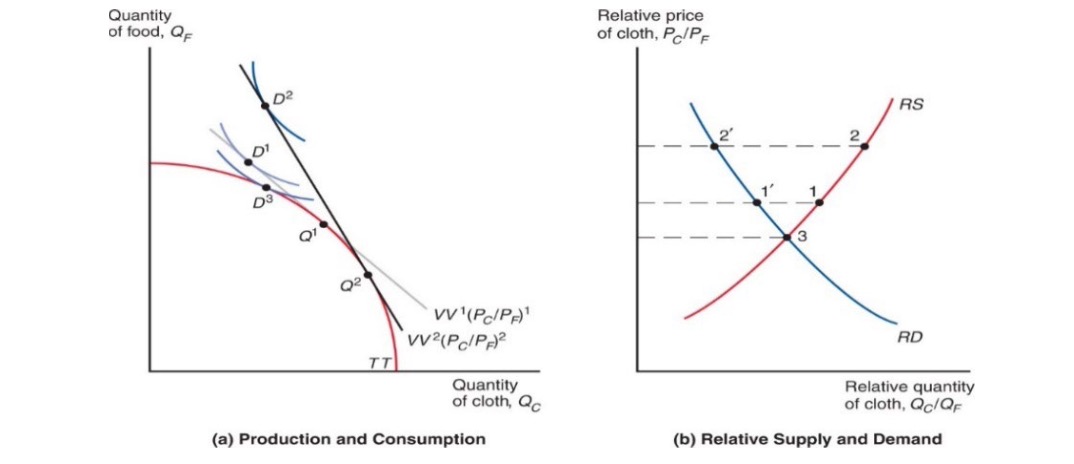
=> Trade = expands PPF
original Point without Trade: \(D^3\)
original Point with Trade: \(D^1\)
Point after Cloth Price Increase: \(D^2\)
Distributional Effects#
Uneven Distribution of Trade Gains
poorer HH = more foods and manufactured
better positioned after trade
richer HH = more services = not exportable
But: Factor Prices (Wages) the other way around affected
Terms of Trade#
Terms of Trade: price of exports relative to price of imports
higher ToT = better for country = afford to buy more imports
Determining relative Prices
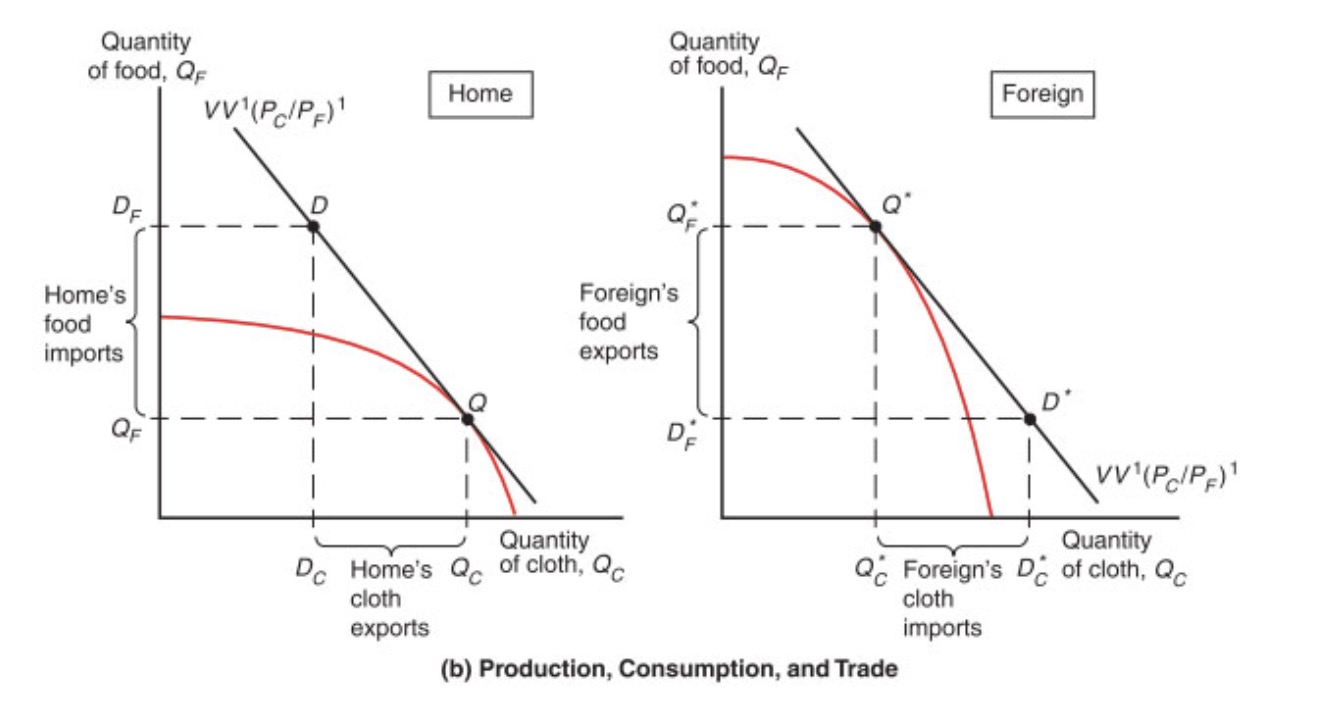
Supply: World Supply of Cloth rel. to world supply of Food: \(\frac{ Q_C+Q_C^* }{Q_F+Q_F^*}\)
Demand: World Demand of Cloth rel. to world Demand of Food: \(\frac{ D_C+D_C^* }{D_F+D_F^*}\)
Situation with Trade
Economic Growth#
is usually biased: one sector more than other
changes terms of trade
example: biased growth in cloth
lower relative price of cloth
lower Terms of Trade
effect depends on if cloth import or export
Type |
Definition |
Effect |
|---|---|---|
Export-biased Growth |
increase PPF mostly in export sector |
reduces ToT = reduces welfare at home |
import-biased Growth |
increase PPF mostly in import sector |
increase ToT = increase welfare |
Instruments#
Import Tariff#
relative price of good (e.g food) rises
more producers into food
lower rel. price of cloth
more consumers into cloth
Effect (from 1 to 2)
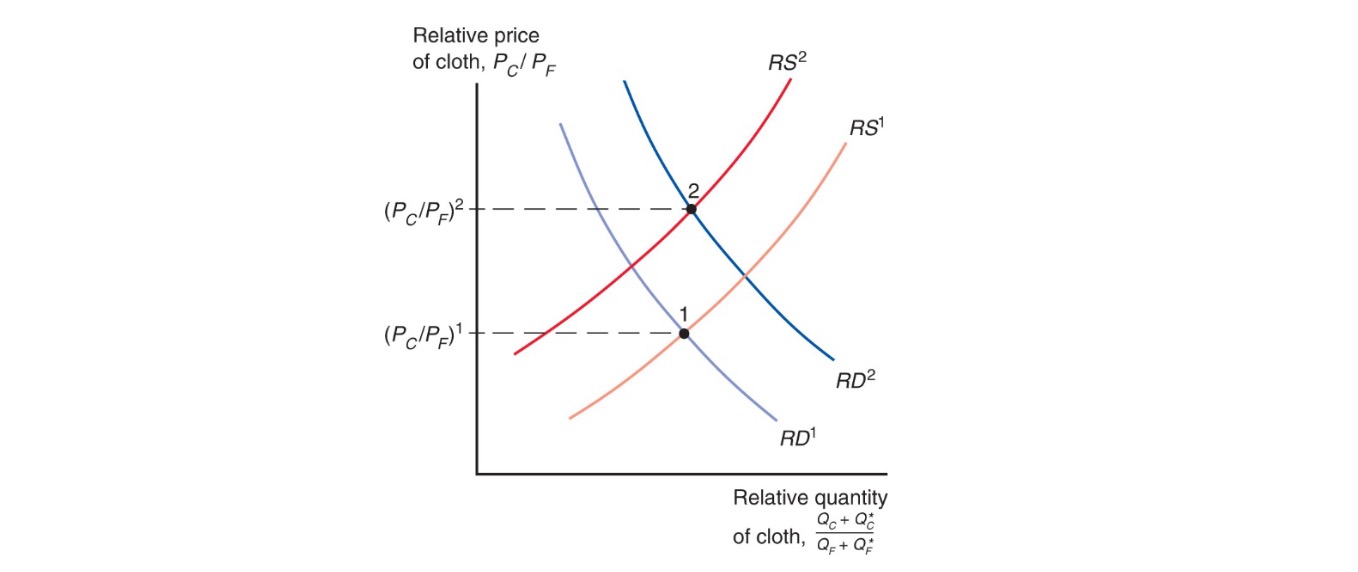
Effect: depends on size of economy in the world trade
Export Subsidies#
e.g subsidy on cloth exports:
rel. price of cloth rises
more producers into cloth
consumers want less
Effect of Instruments#
Import tariff: can increase domestic welfare
export subsidy: reduce domestic welfare
Additional Effects
another Foreign Country makes export subsidy
If home country also exporter = less competitive
reduces home ToT
Tariff vice versa = more ToT if both countries same role (import / export)
Export subsidies and Import tariffs:
reduce world prices for other countries (more supply / less demand)
better ToT depends on home countries role
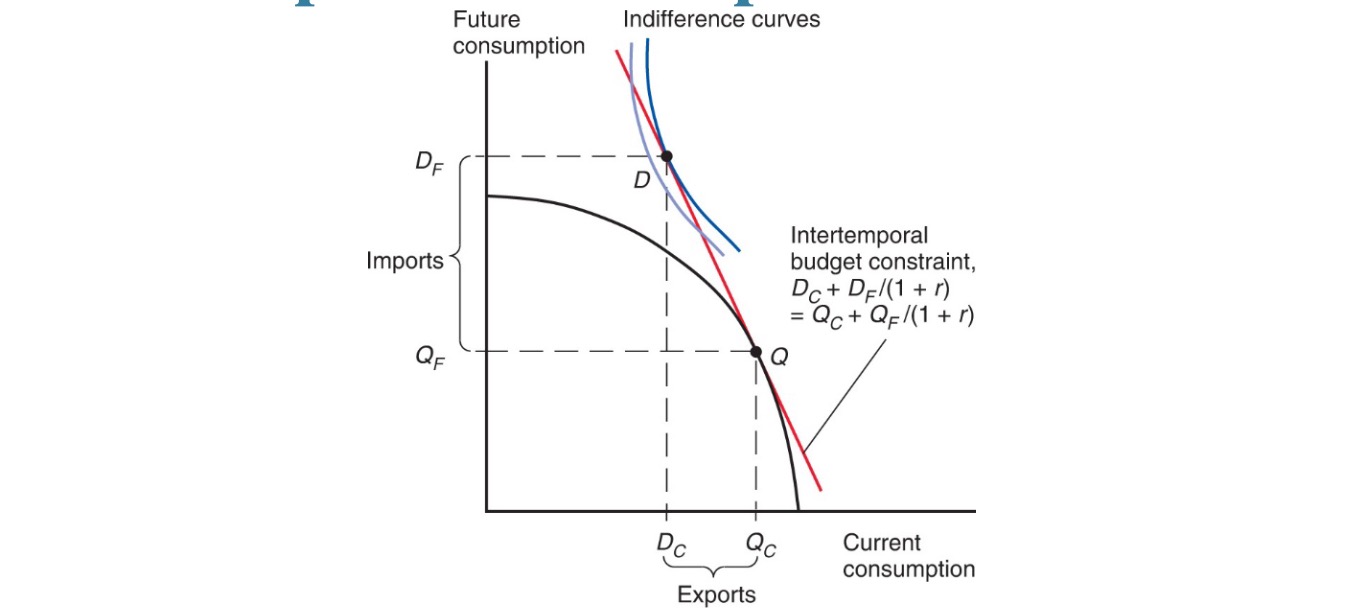
Borrowing and Lending#
Countries maximize intertemporal consumption
produce more this year, consume more next year
then lend money to other countries this year and borrow next
=> interest rate globally come closer