24.05.2023 Fiscal Policy#
Aggregate Demand#
Aggregate Consumption
autonomous consumption = fixed amount based on future income
slope of function = marginal propensity to consume
additional consumption based on more income in period etc
45° Line where AD = Aggregate Output
state of normal economy
Investment: does not depend on output
added to AD Line
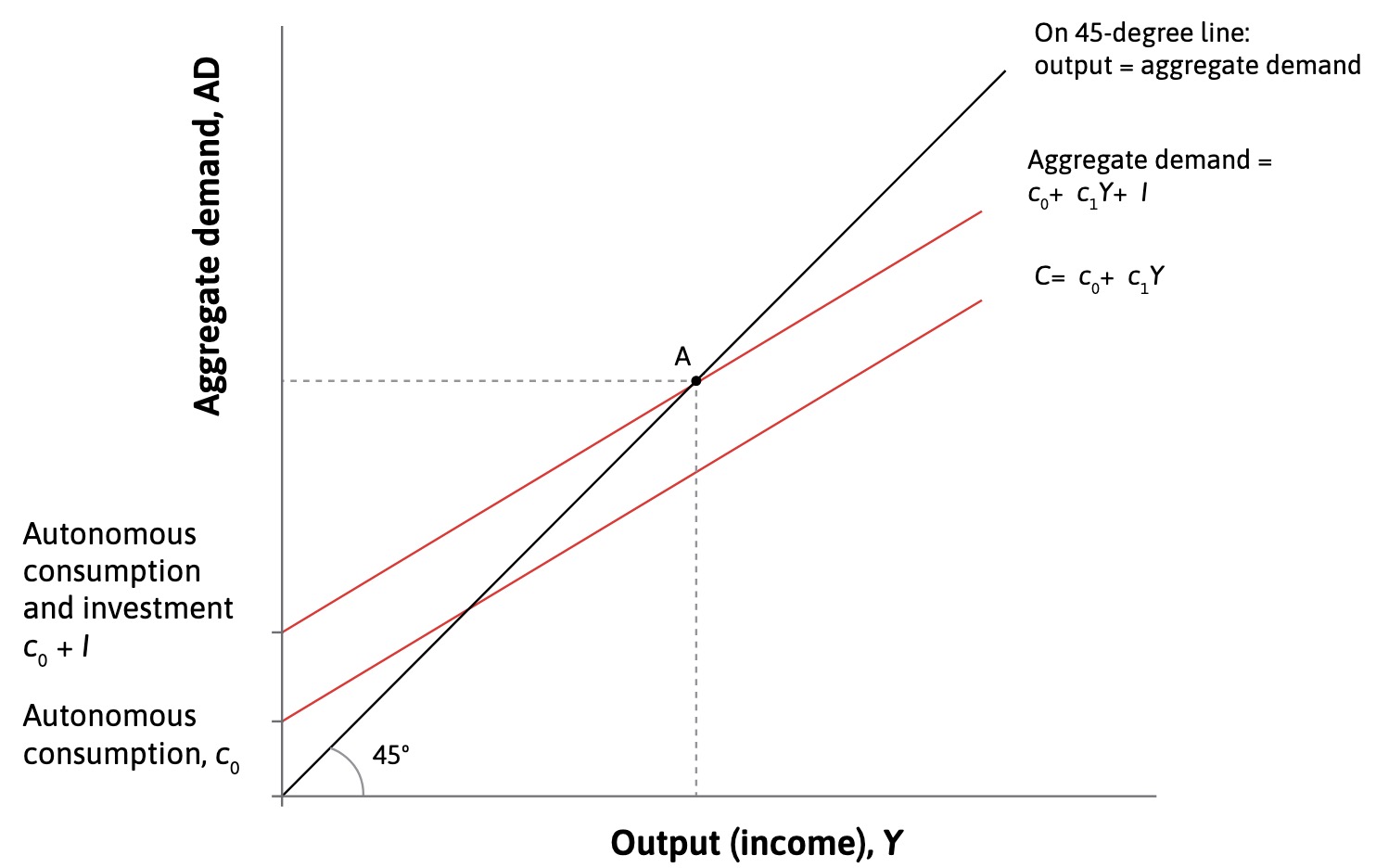
implicit assumption: underutilized capacity in economy
The multiplier#
A Decrease (or Increase) in Investments leads to a higher decrease in Income than the original
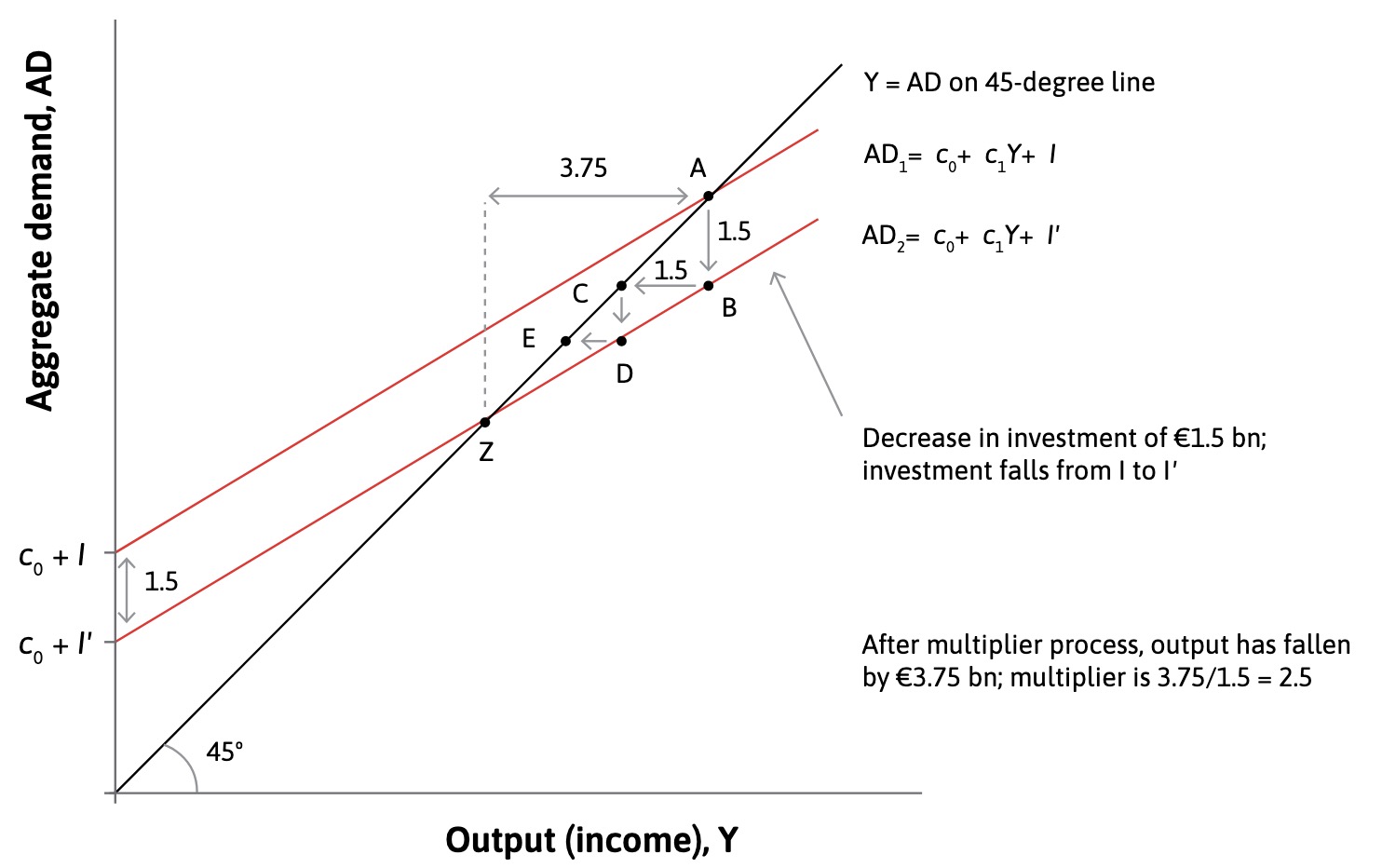
original negative investment = 1.5bn€
expected point afterwards = C
but households now have less money and this leads to ripple effects = Z
Determining the Multiplier
with \(c_1\) = marginal propensity to consume
Household Spending#
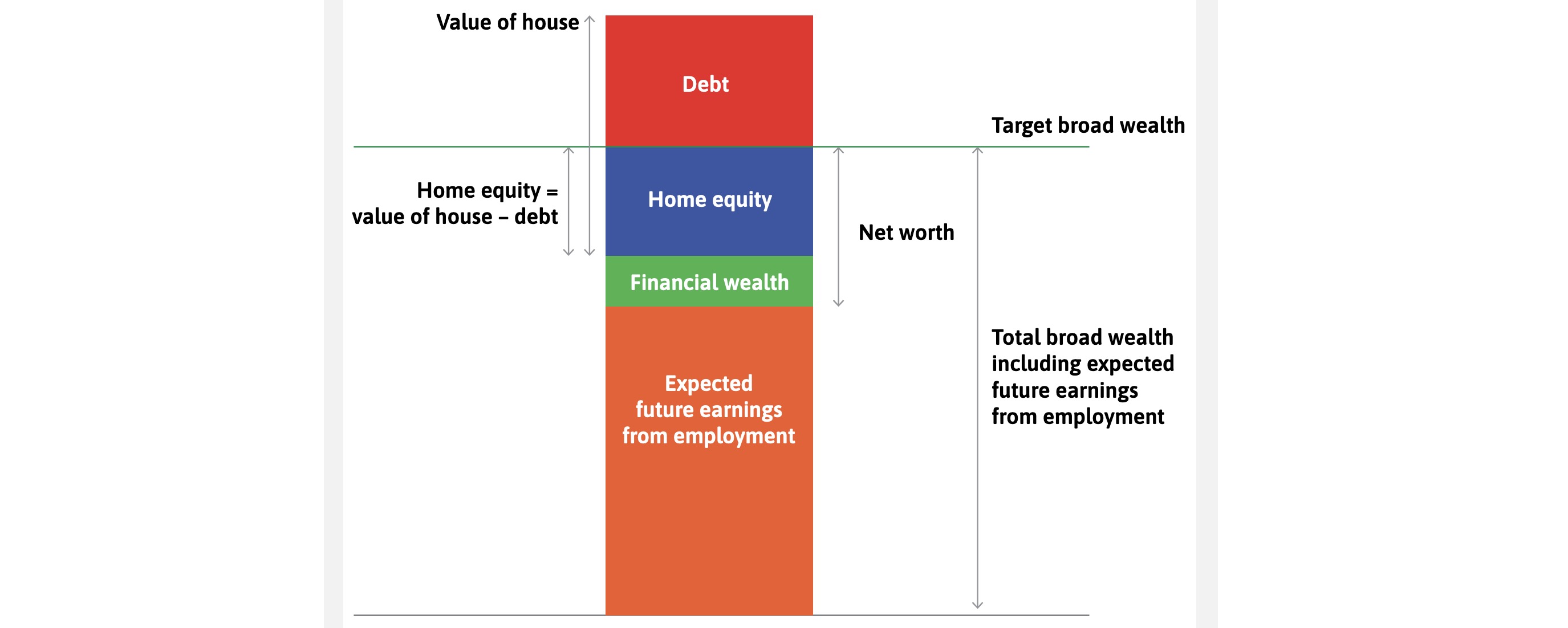
Has Target Wealth: level to maintain based on expectations
optimizes broad wealth: assets - debt, including future earnings
Paradox of thrift (Sparparadoxon): aggregate attempts of all households to increase savings during a recession does not actually increase savings
Autonomous Consumption declines => AD curve downwards
Income + Labor Demand declines => Recession
higher savings at lower income = absolute lower savings
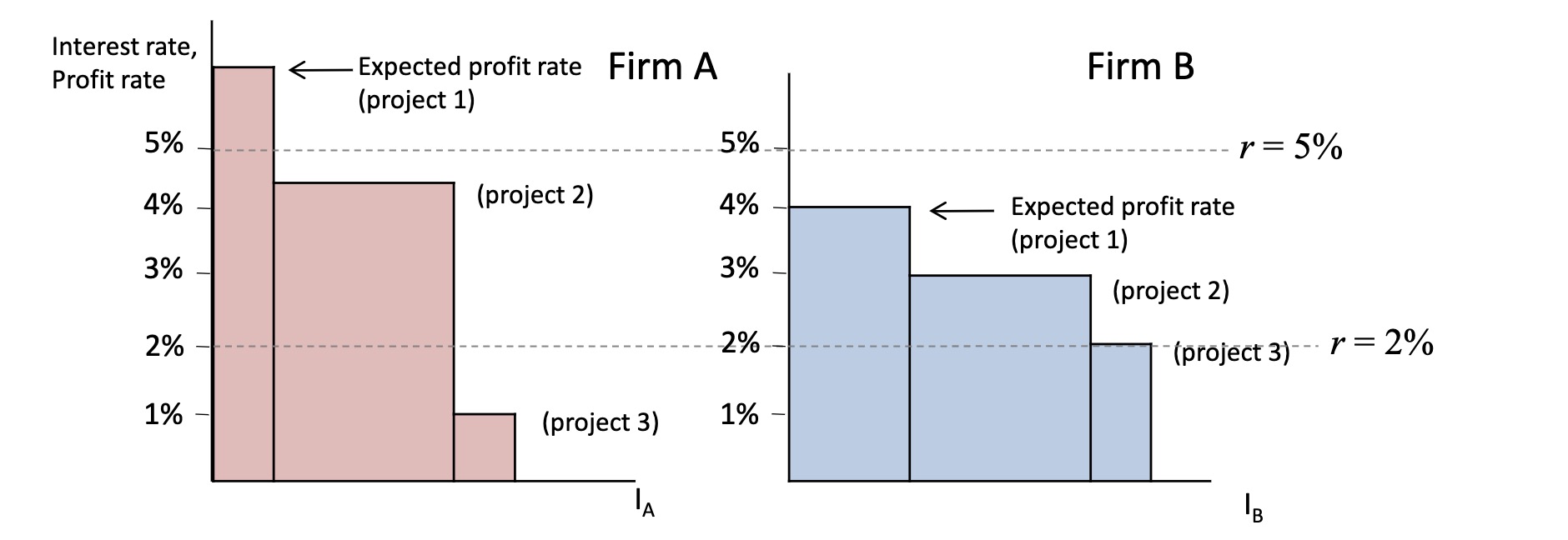
Firms Investments#
Decicsions depend:
Discount rate p of owner (opprt. cost)
interest rate r
profit rate of investment \(\Pi\)
Investment when: \(\Pi > p+r\)
Example: individual firms
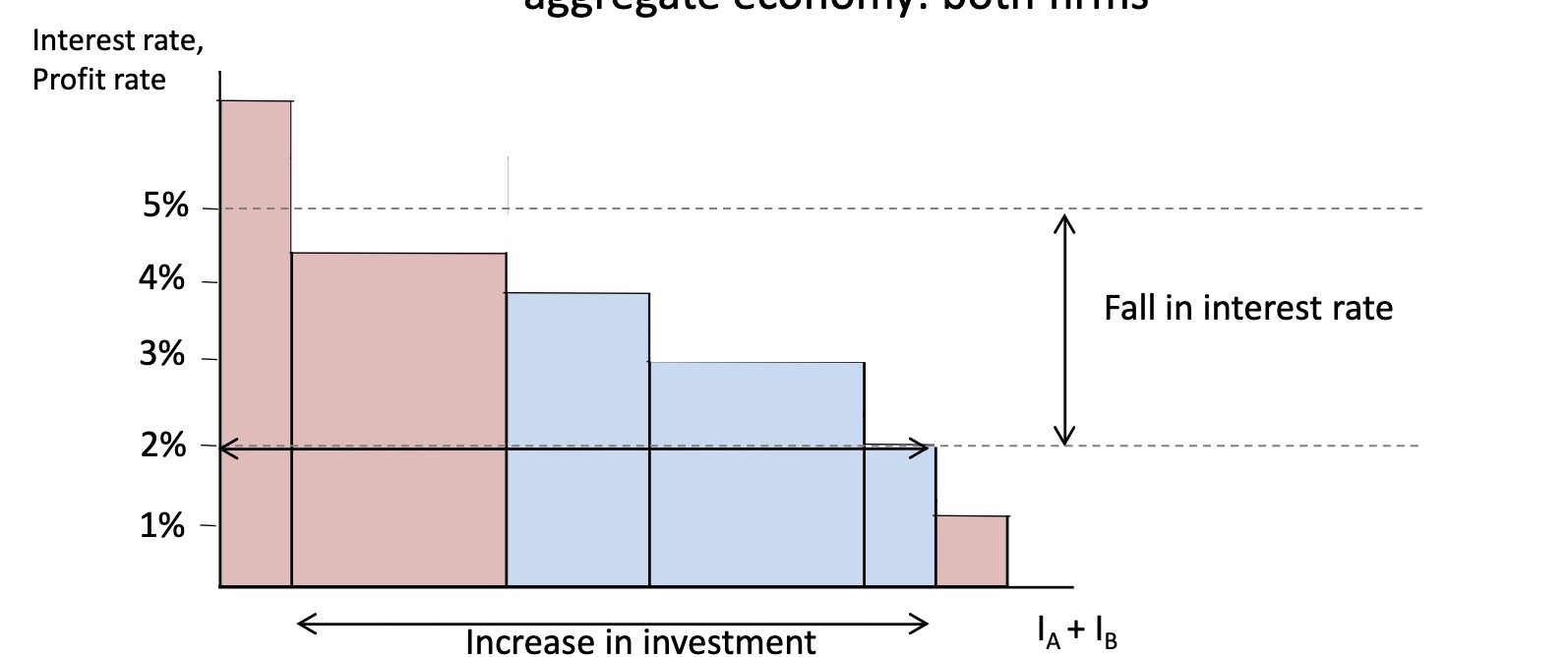
The Aggregate Economy: sinking interest rates = more Projects
Government and Imports#
Government Spending and Net Exports = shift 45° Line up
marginal propensity to import (m): fraction of additional dollar spend on imports of household
Net Exports \(= X-M = X-mY\)
Combined Formula
With t = Tax rate
Fiscal Policy#
How does Government Policy impact Aggregate Demand and the Business Cycle?
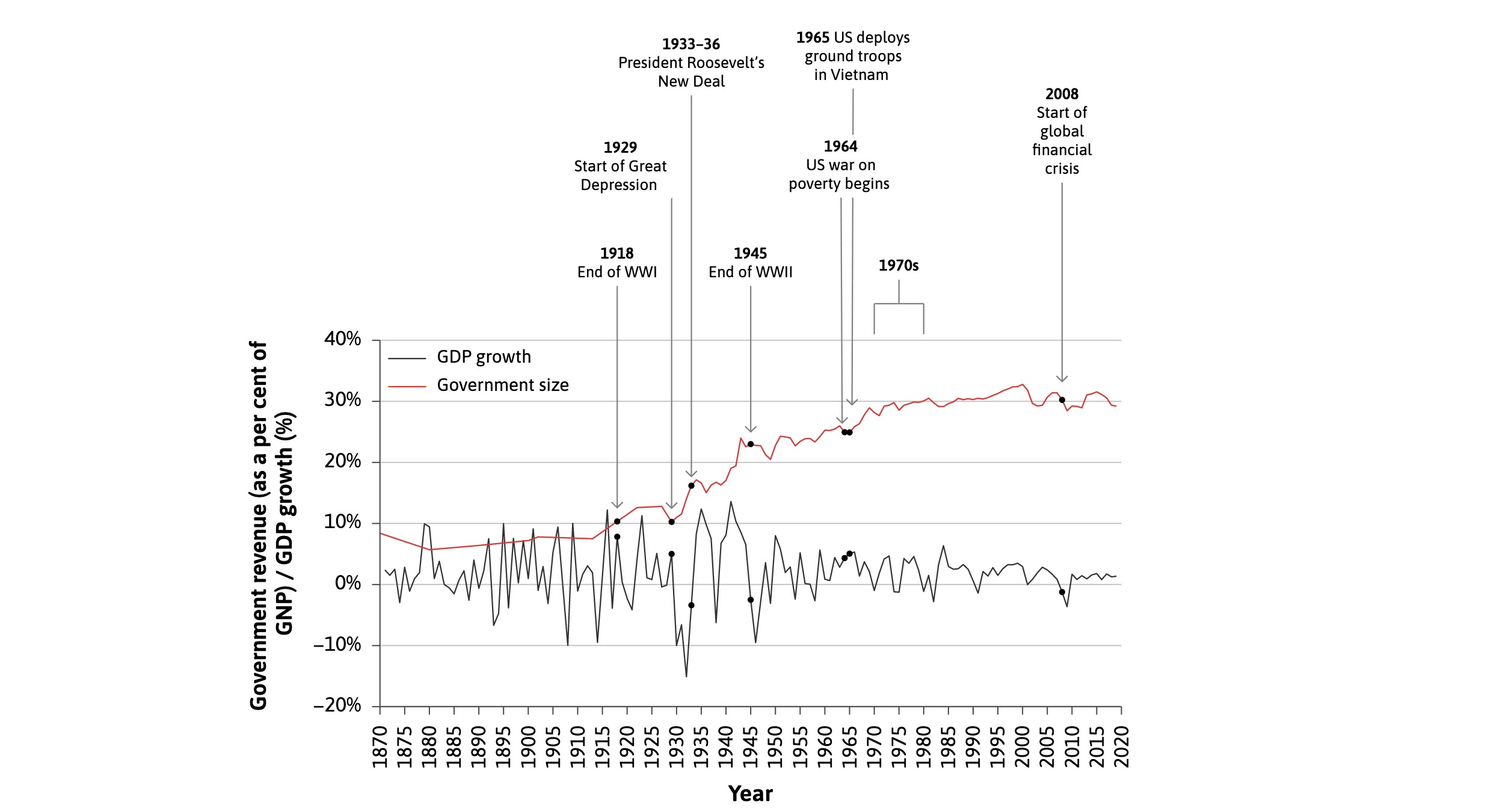
=> severity of Business cycle shrinked with bigger government
Policy before Keynes#
after David Ricardo:
wages and prices adjust
no long-term disturbances
only role of government = avoid deficits
=> orthodox policy = austerity
Economics: Allocation of scarce resources
Policy after Keynes#
in the long run, we’re all dead
government intervention can provide benefits to society
due to the money multiplier
the effect of fiscal stimulus is more than the money used for it
Economics: study of how agents allocate resources and how those choices affect society
Government Role#
Stabilizing
non-cyclical expenditures (education)
income redistribution (consumption smoothing)
investments in recessions
Destabilizing
trough Austerity in Crisis
political business cycle
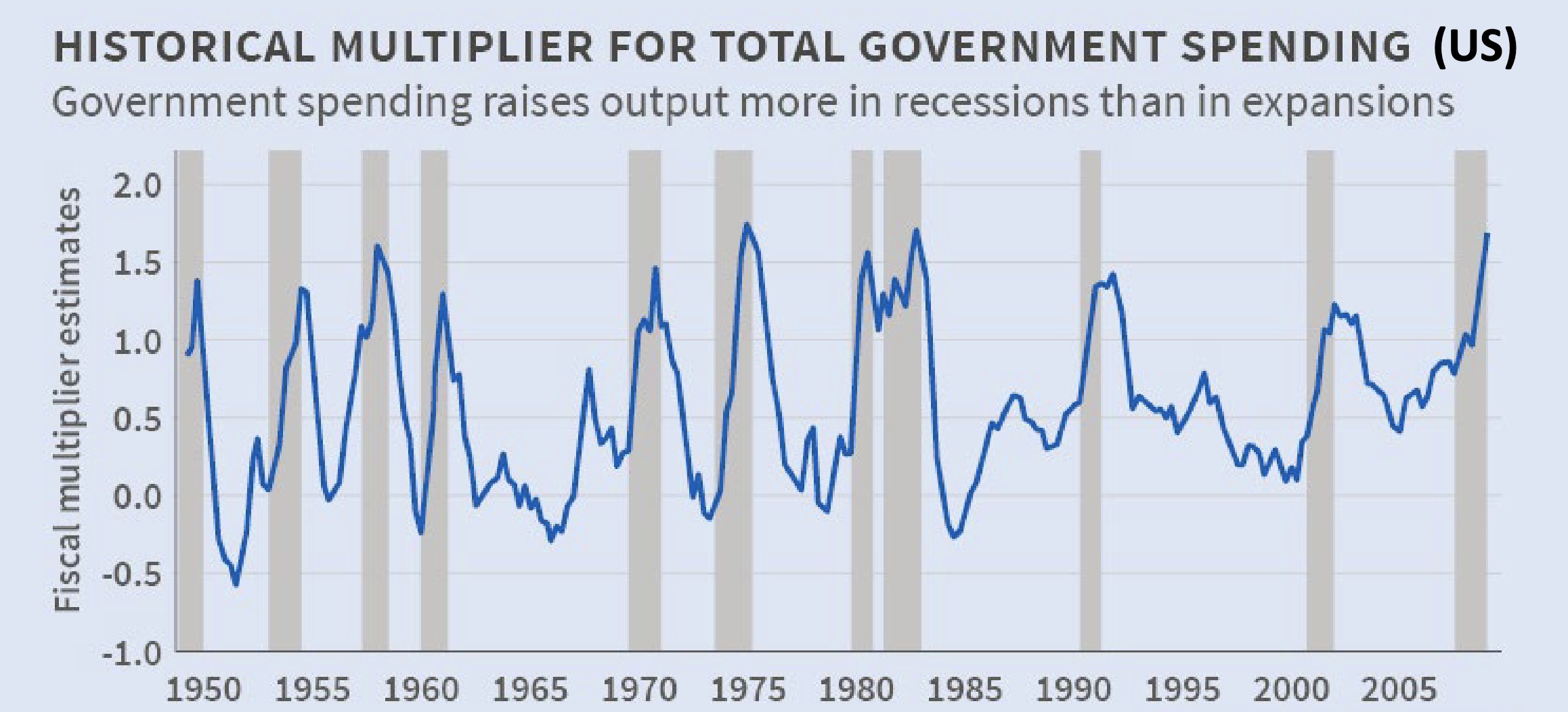
Depends on Multiplier:
empiric research suggests: multiplier in crisis is above 1 (even IMF says so) and austerity is therefore a very dumb idea…
The Multiplier over the business cycle:
in crisis: high because of anticipation and underused capacity
in booms: lower (but often above 1)
Governments finances#
Revenues |
Expenditures |
|---|---|
Income Tax |
social transfers |
Value Added Tax |
public investment |
Inheritance Tax |
interest |
Definitions:
primary budget deficit: revenou minus expenditures (excl. interest)
sovereign debt crisis: situation, where gov. bonds are deemed to risky, -> not abel to borrow
Instruments for sustainable debt:
running surplus (in booms)
creating inflation
benefitting g > r
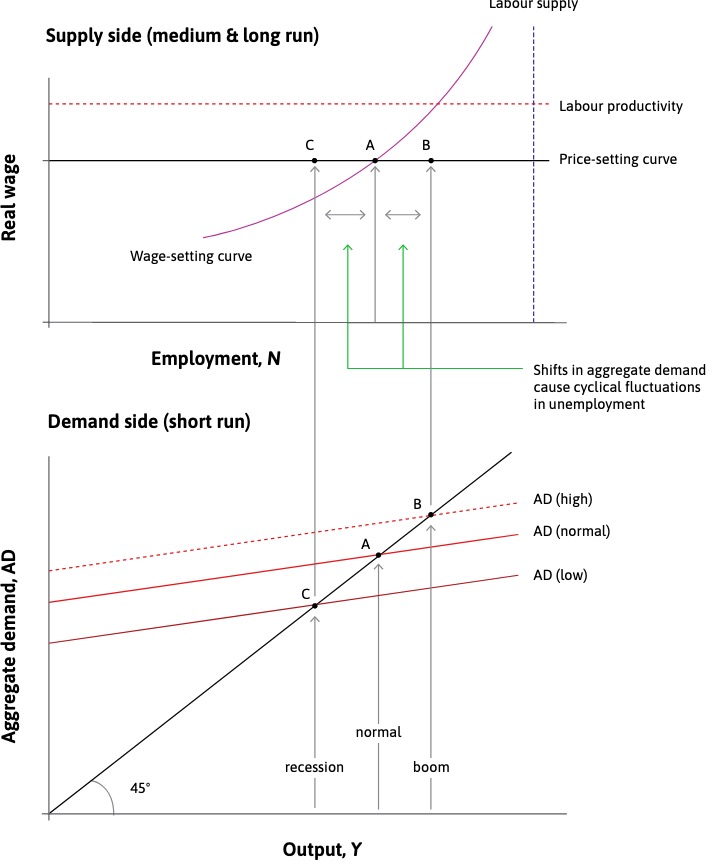
AD and unemployment#
Supply Side |
Demand Side |
|---|---|
labor market model |
multiplier model |
Medium-run: wages + prices change, all other const. |
short run: employment changes, al other fixed |
|
|
Connected by: production function
N = employment
\(\lambda\) = labour productivity
both connected:
shifts in AD: cyclical changes in employment (but not curve shifting anywhere)