12.07.2023 Political Economy#
Arguments#
Case for Free Trade#
lower prices
efficient allocation, competition
economies of scale
Case against Free Trade#
better terms of trade trough tariffs
big country can be beneficial
optimal tax rate and export subsidy exists
domestic market failures (unempl. underutilization)
But: unintended consequences, market failures other options better
Political Model of Trade Policy#
Median Voter#
Assumptions:
Two-Party Democracy
Obejctive: majority vote
Parties in Democracies pick position of voter in middle of political spectrum
Effect should be: Consumers > producers, free trade
Collective Action#
a group has incentive to advocate for issue, but each individual close to no incentive
e.g consumers can save big money, but each individual consumer only 10 cent
Therefore special interests > collective action
International Politics#
since 1944 reduction of tariffs
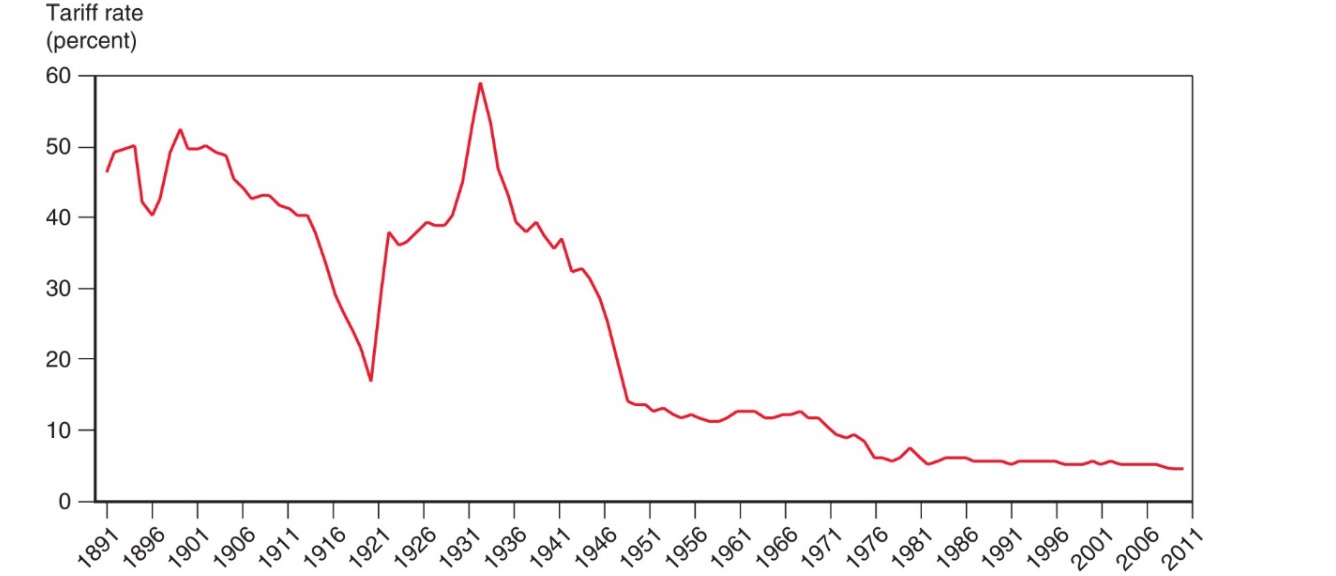
General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade (GATT) 1947
World Trade Organization (WTO) 1995
to stop trade wars with shared rule book
WTO#
World Trade Organization
WTO Rules:
reducing tariff rates
bind tariff rates
eliminate nontariff barriers
Elelements:
GA on Tariffs and Trade
GA on Tariffs and Services
GA on Trade-Aspects of Intellectual property
Dispute settlement procedure
Preferrential Trading Agreements#
Agreement, where one country pays less than rest of the world
under WTO Rules generally not allowed, except
Free Trade Area: each country own trade policy (NAFTA)
Customs Union: common trade policy (EU)
but not always beneficial