14.04.2023 Labour Market#
Unemployment: people who are without work for longer period and seeking new employment
Definitions:

The Labour Market#
Wage Setting: takes place in the firm: wage above unemployment rent
beased on unemployment rate
other firms wages
Price Setting: as markup above cost of production
other firms prices
own costs and wages
position of demand curve (elasticity)
=> adding up decisions = real wage and unemployment rate
Decision Process
Department |
Knows |
Sets |
|---|---|---|
HR |
prices, wages, unempl. Rate |
nominal Wage W |
Marketing |
demand curve position |
Price of output p |
Production |
labor productivity |
Employment n |
Procution Function of Firm: $\( Y = \underset{labor\ productiity}{\lambda} \cdot \underset{workers}{n} \)$
Wage Setting Curve#
Wages in aggregate economy:
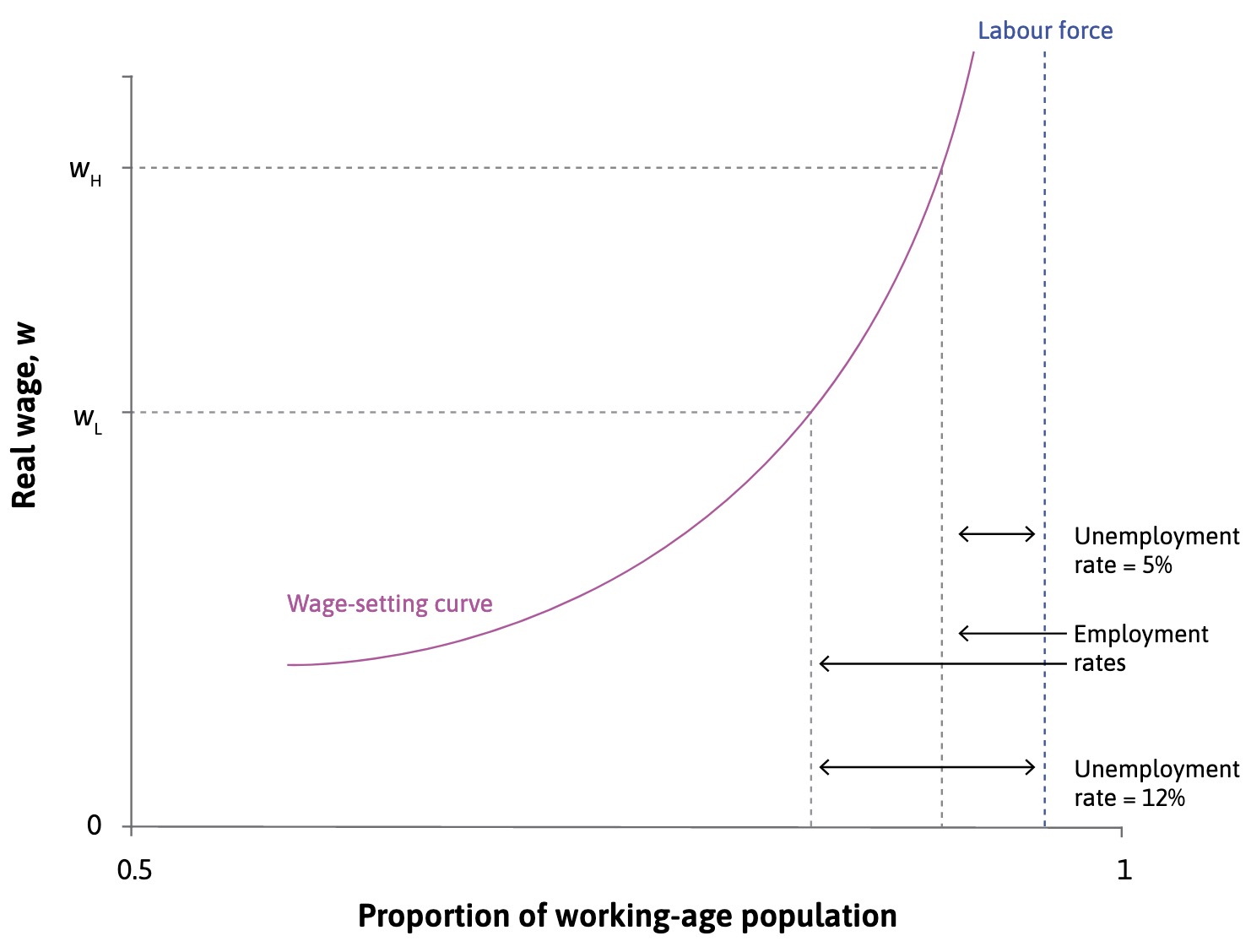
Influences:
unemployment benefits -> curve upwards
labor supply increases -> curve downwards
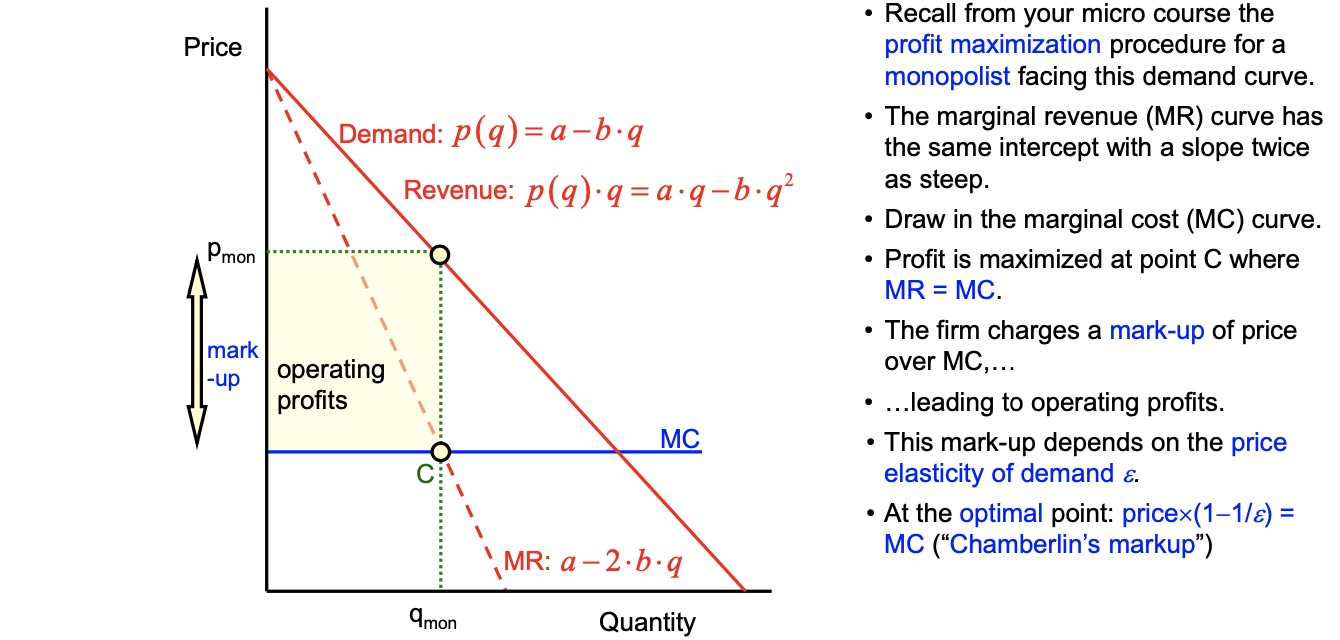
Isoprofit Curve#
Firm maximizes profit
based on elasticity of demand (inverse)
and level of competition (inverse)
leads to price setting curve: (p.w. = per worker) $\( \implies \underbrace{\frac{W}{P}}_{real \ Wage} = \underbrace{\lambda}_{output \ p.w.} - \underbrace{\lambda \cdot \mu}_{real \ profit \ p.w.} \)$ note:
wage = \(\lambda\)
high competition = low \(\mu\) = high wages
Price Setting#
based on Monopolistic Competition
markup depends on level of competition in market
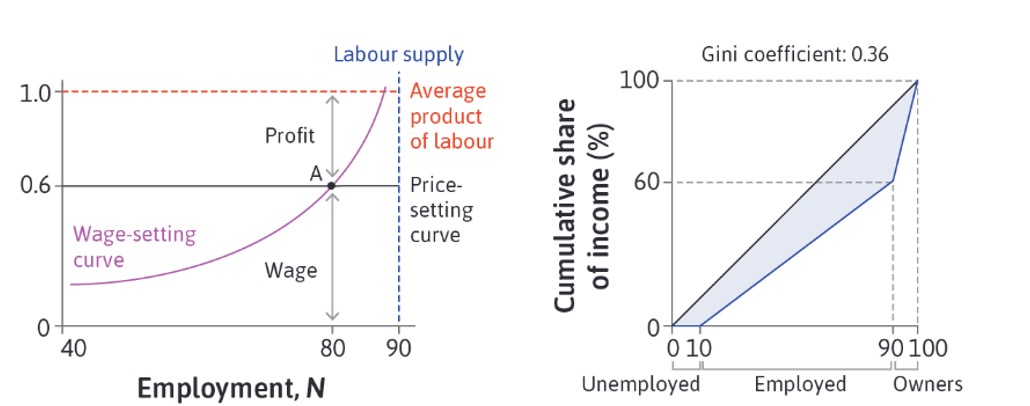
Labour Market Equilibrium#
lecture from 20.04.2023
wage-setting curve: wage required at level of empl. for effort
Price-setting curve: real wage based on comp, productivitiy
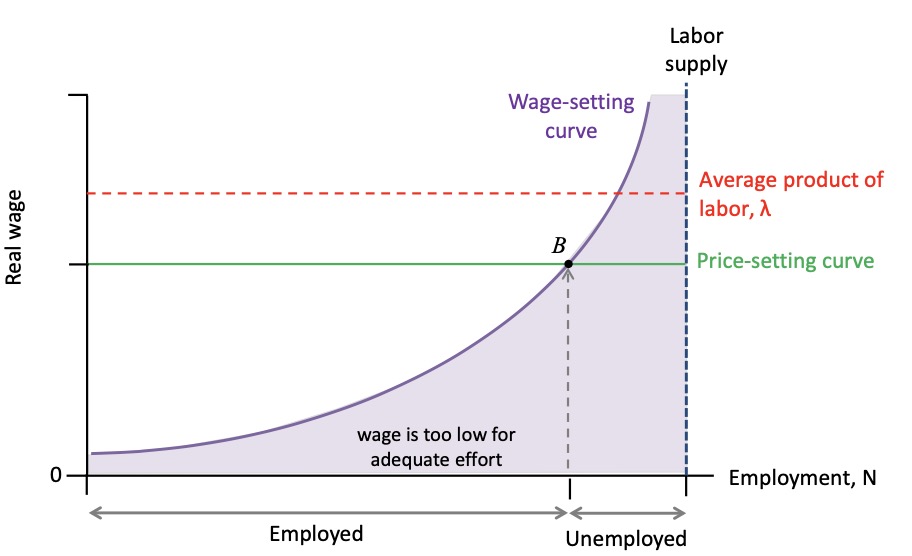
Nash-Equilibrium:
firms offer least wage for effort
employment highest it can be
unemployed cannot imporve situation
leads to:
Involuntary Unemployment#
involuntary unemployment: people at working age willing to supply labor but not finding a job
excess supply in labor market
always exists
due to incomplete contracts, not policy!
Demand and Unemployment#
Firms labor demand depends on Demand for Goods => derived demand for labor
depends on aggregate demand
Fall in AD => demand-deficient unemployment
theory:
firms adjust wages to lower point
lower costs -> lower prices
increased output
reality:
no cuts to wages
lower wages = less AD
falling prices = deflation
=> Government Intervention helps
Inequality#
lecutre on 21.04.2023
Labor Market = Division of Output
employed
unemployed
Firm-owners
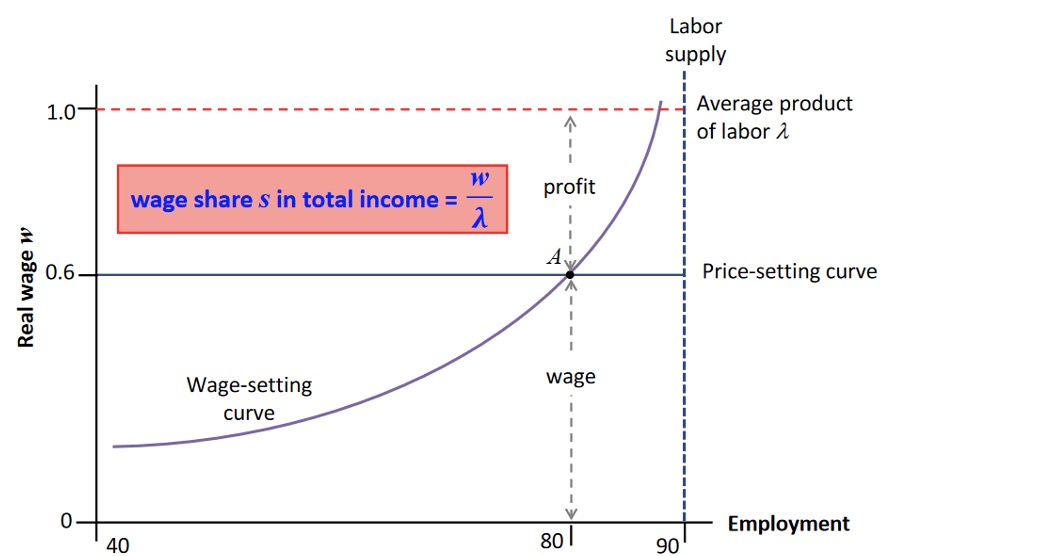
Measuring Inequality#
Lorenz Curve:
Gini Coefficient: Measure of Ineq. from 0 to 1
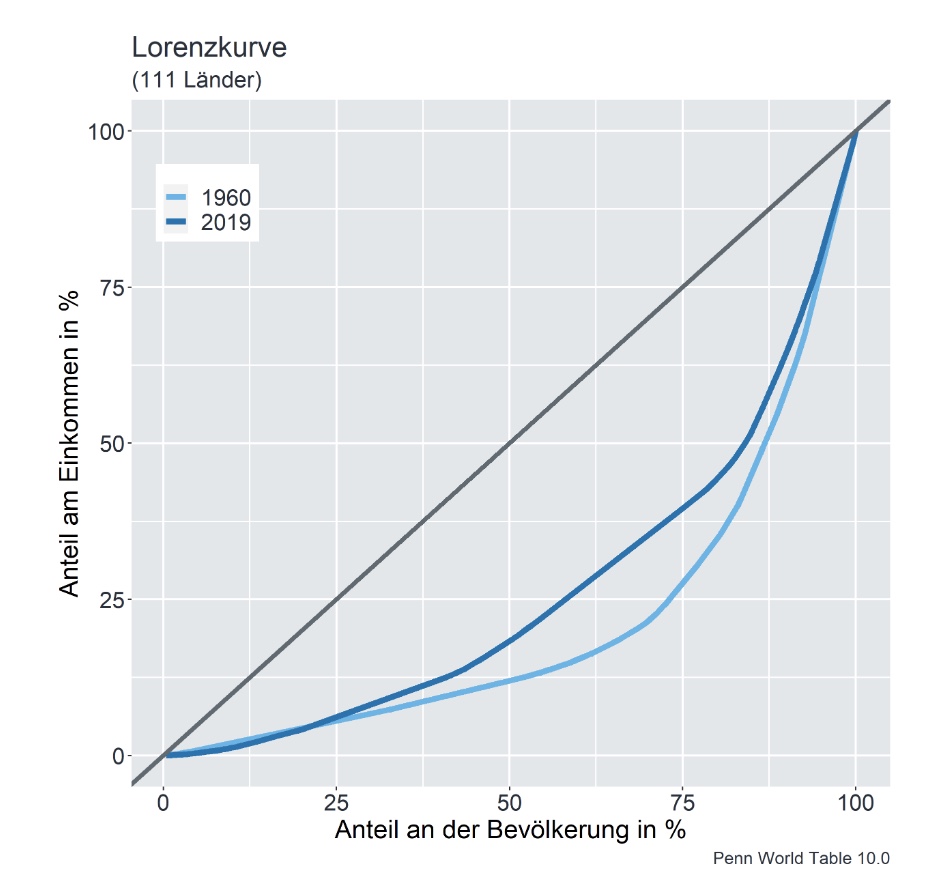
Calculating Gini:
\(G = \frac{1}{2*n^2*u} \sum_j \sum_i n_j * n_i * | y_j - y_i |\)
\(G = \frac{A}{A+B}\)
Principles of an inequality measure
Anonymity : insensitive to permutations (change of rich to poor etc.)
Population: Clone / Double Population = no effect
Dalton: Transfer from rich to poor = no effect
relative income principle: double all incomes = no effect
Lorenz for given example with workers:
mean wage employed: \(\frac{0.6}{80} = 0.0075\)
mean wage capitalists: \(\frac{0.4}{0.1} = 0.04\)
\(u = \frac{10*0+80*0.0075+10*0.04}{n=100} = 0.01\)
Effects on Inequality#
rises with:
Unenplyoment rate \(\uparrow\)
productitivity \(\uparrow\) at constant wage
number of employers = market power \(\uparrow\) = lower wage \(\downarrow\)
Global Inequality#
How did Globalistaion effect Ineq.?
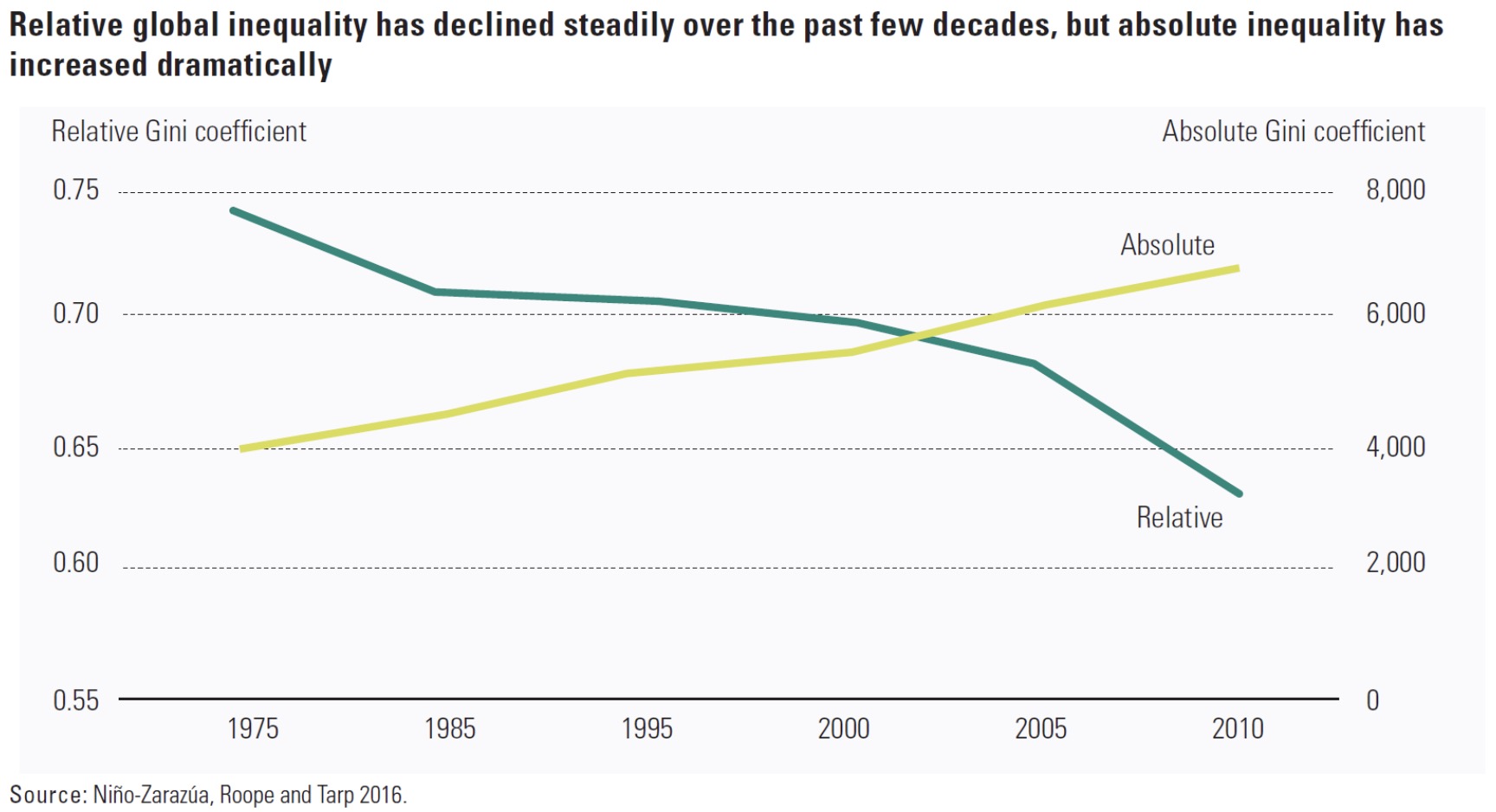
Why:
high rates of growth
especially populous southeast (China)
Redistribution#
Market Income is very inuequally distributed
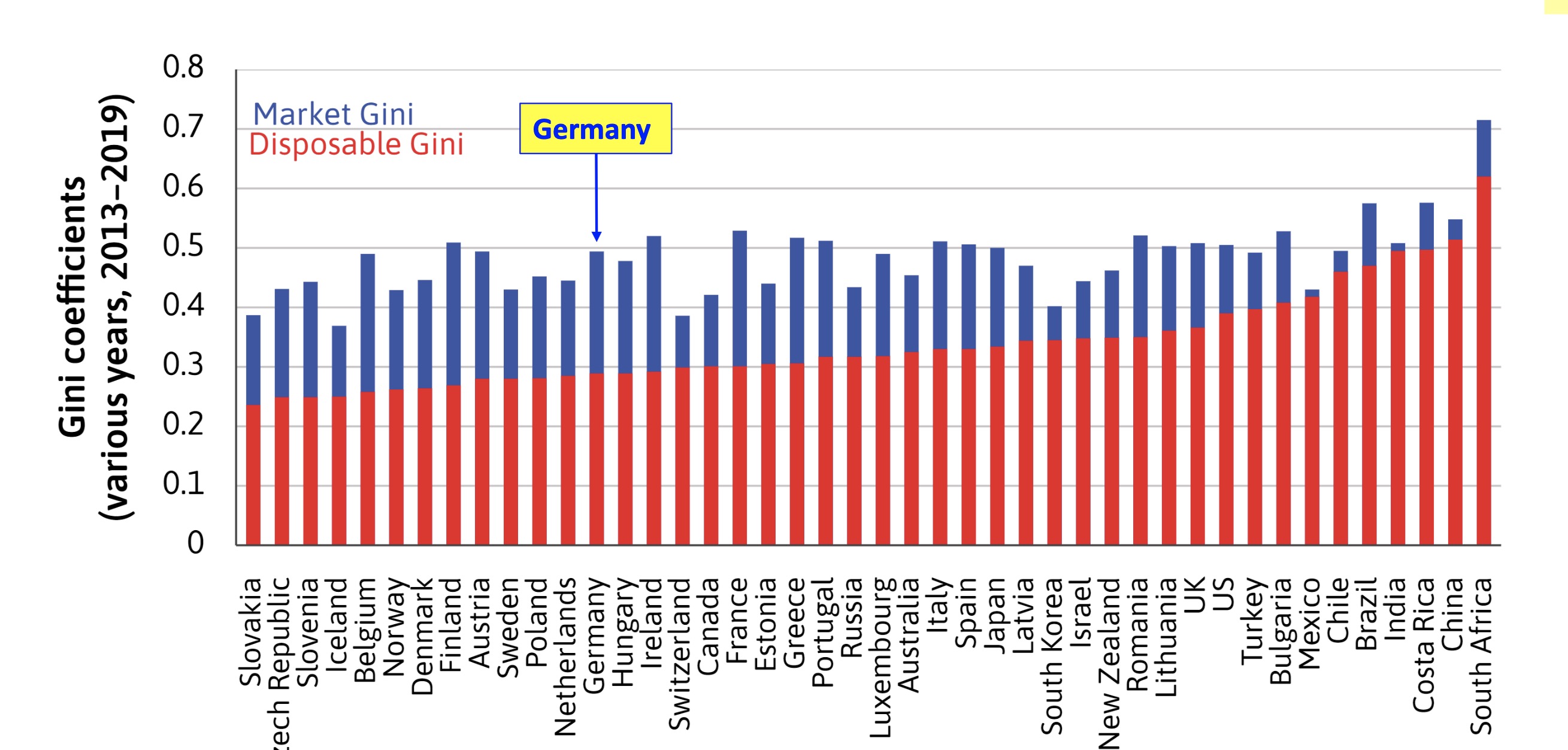
but Redistribution leads to more equal societies!