11.05.2023 Specific Factor Model#
Model that allows income to be a part
Assumptions#
two goods: cloth and food
tree factors of production: L, K, T (land)
perfect competition
Definition#
Cloth Inputs: Capital + Labor (not Land)
Food Inputs: Land + Labor
Labor = mobile factor
more people employed in one production = more output
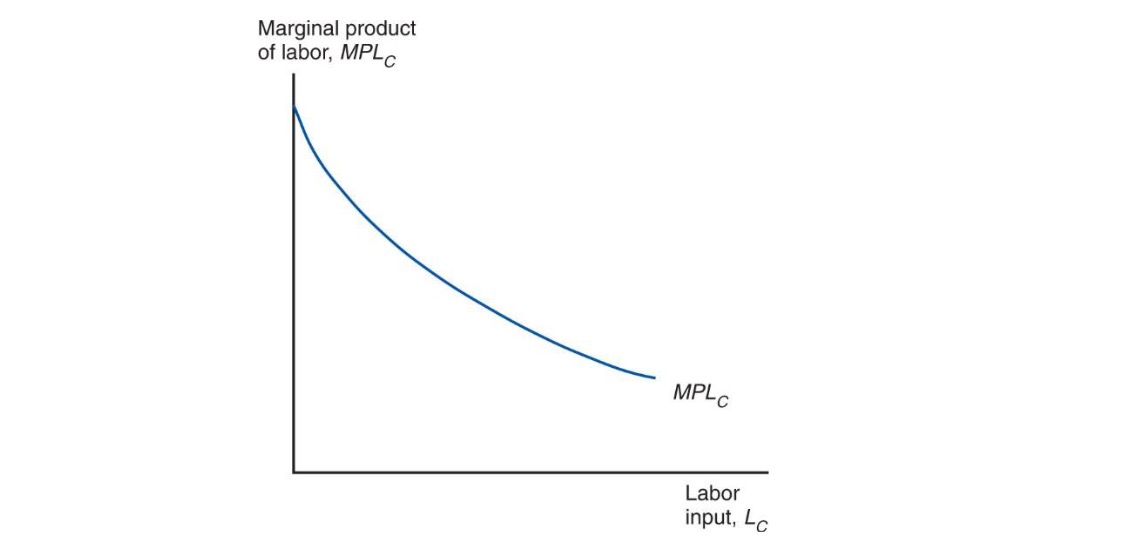
but diminishing returns
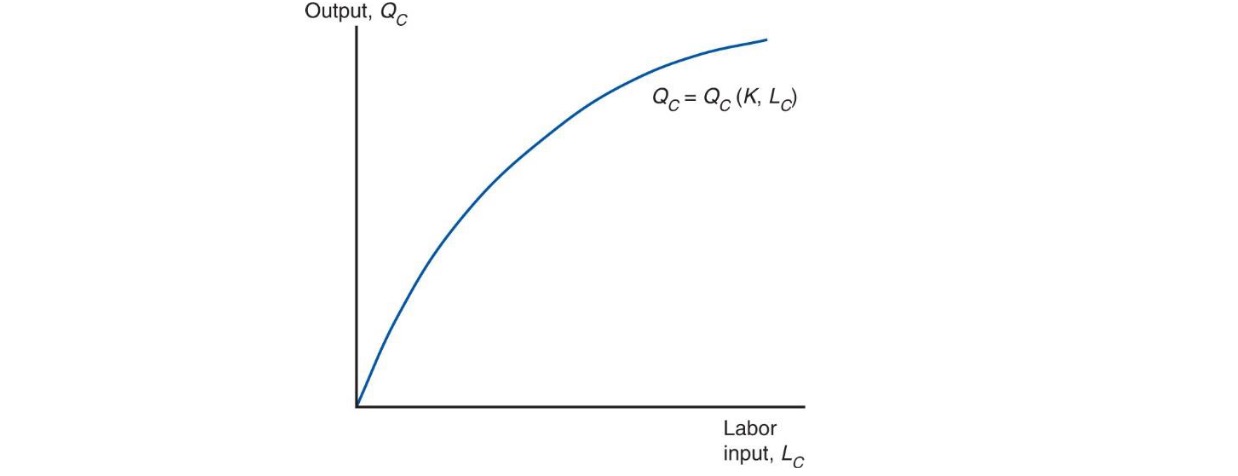
Marginal Product of Labor:
Production Possibilites#
Labor split between Sectors
\(L = L_C+L_F\)
Four-Quadrant Diagram for PPF
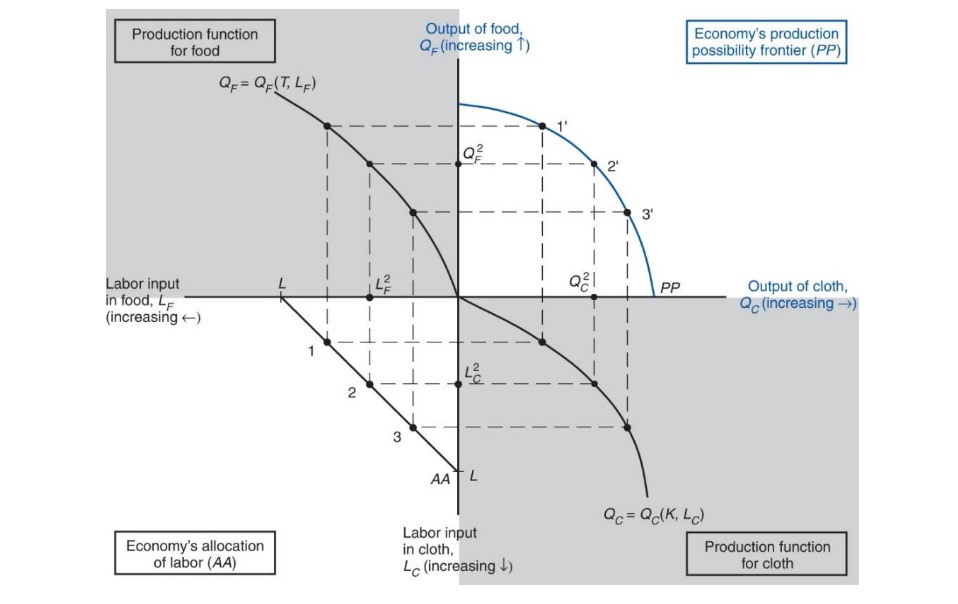
Quadrants:
lower left: Allocation of Labor
lower right: Production Cloth
upper left: Production Food
upper right: combinations of both
PPF sloped because of diminishing returns
opprtunity Costs of one more cloth
is \(\frac{MPL_F}{MPL_C}\) pounds of food
need \(\frac{1}{MPL_C}\) hours of labor
to free up one hour: reduce food by \(MPL_F\) units
Result:
\(MPL\) in Food rises (less workers there)
MPL in Cloth falls (more workers there = each less productive)
\(\frac{MPL_F}{MPL_C}\) rises
Labor Allocation#
How much labor in each sector?
Demand: where MPL of one hour = Marginal Cost of one hour $\( W = MPL_C \times P_C \\ W = MPL_F \times P_F \)$
two sectors must pay same wage (mobility)
Demand for Labor = \(MPL_C\) (second Figure) times \(P_C\)
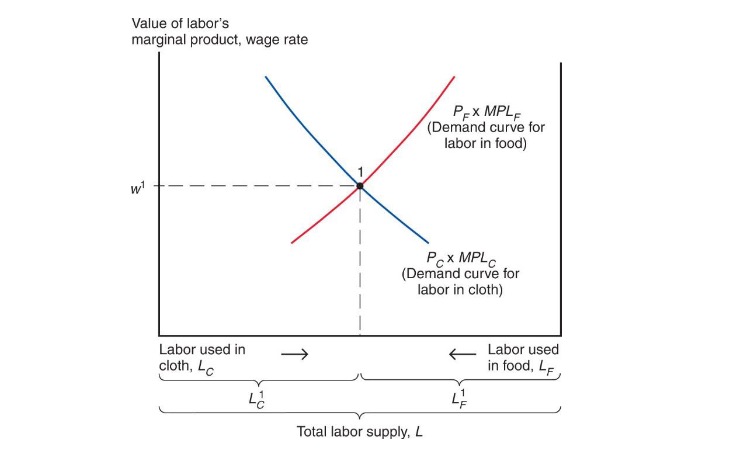
Wage = Equilibrium
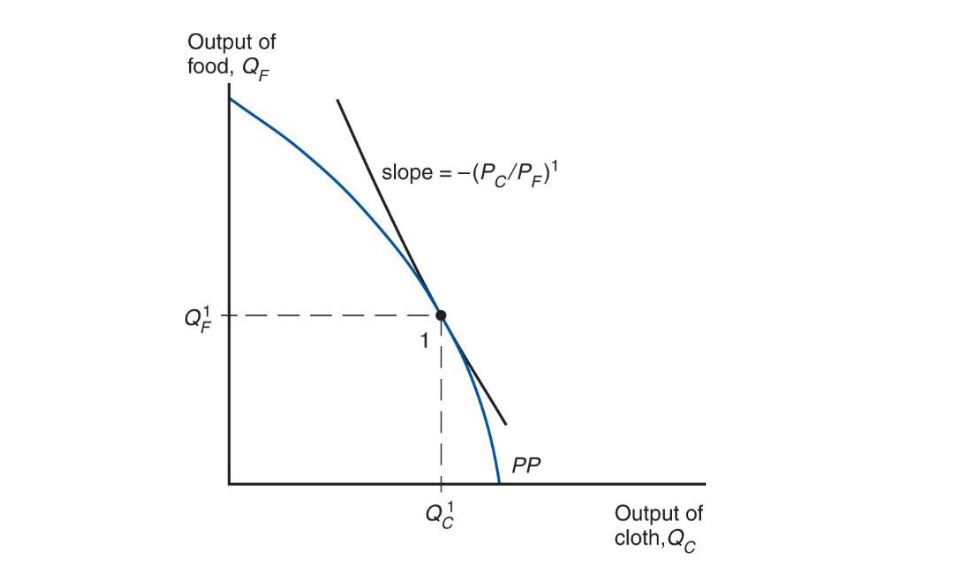
Production#
at Production Point: PPF tangent to relative Prices
$\(
-\frac{MPL_F}{MPL_C} = - \frac{P_C}{P_F}
\)$
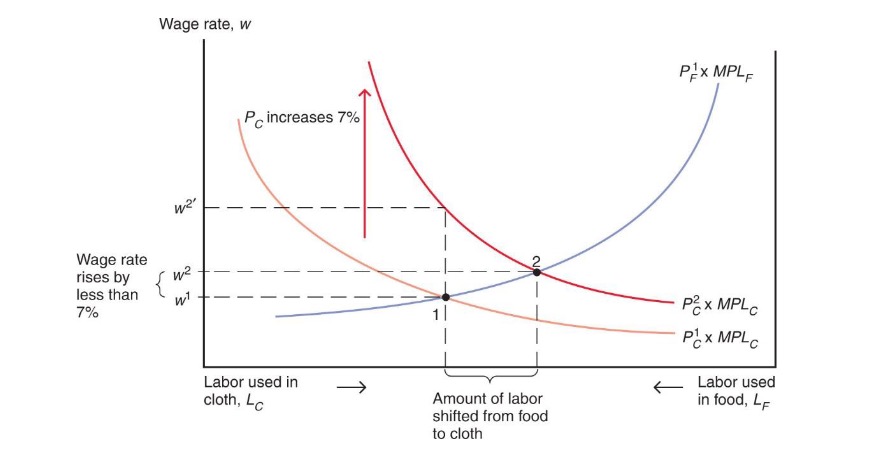
Shocks#
Change in relative Prices (not equal in goods)
If \(P_C\) rises:
labor shifts to Cloth Sector
Output of Cloth Sector rises
w rise not equal to rise in prices
Employment Increase = MPL falls
higher cost of employment
Economic Effect:
Capital owners = profits rise
Land owners = less profits
Workers = depends
relative preference of cloth and food
International Trade#
Price determined by Relative Supply / Demand
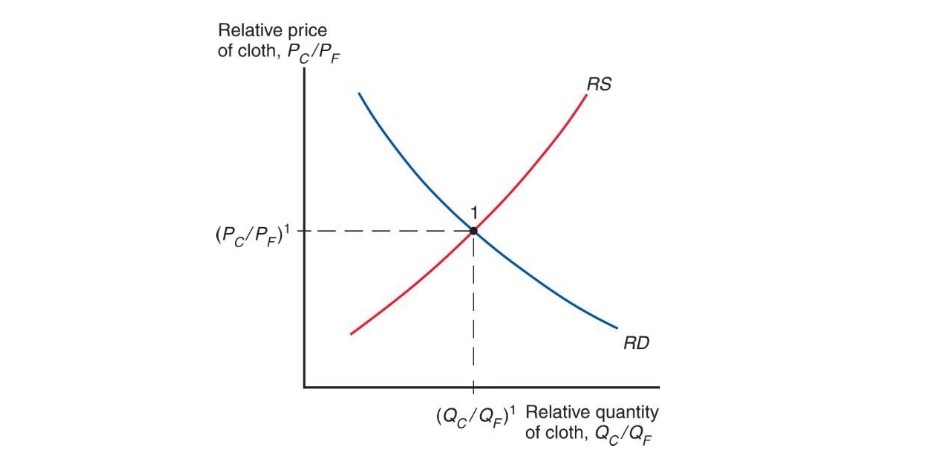
Opening up:
if RS in economy > RS in world economy
=> price increase
Gains from Trade:
allows mix of consumption
different from production
but spending = income from production
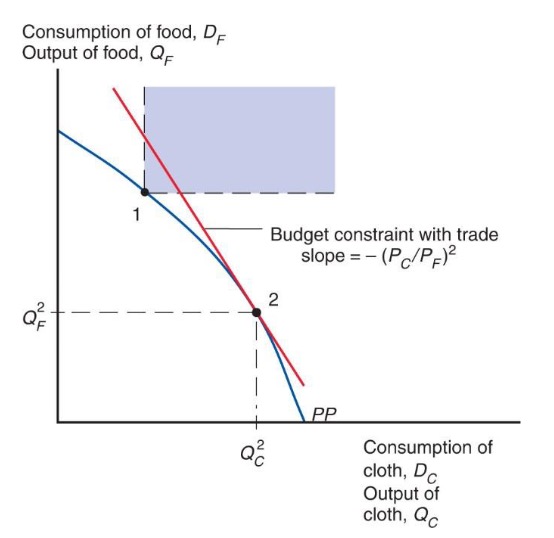
Economy as whole profits
Budget Constraint above PPF
But:
profits the non-mobile factor (K / T) of export sector
mobile sector = ambiguos
produces losers and winners (consumers)
often hurts relatively poor workers (garment workers in DE)
=> Redistribution from winners to losers
Unemployment#
International Trade:
Shifts jobs from import-competing to export sector
temporary unemployment
but unemployment = mostly macroeconomic
Instruments:
extended unemployment benefits
skill acquisition financially supported
Exercise#
\(w = MPL * P\)
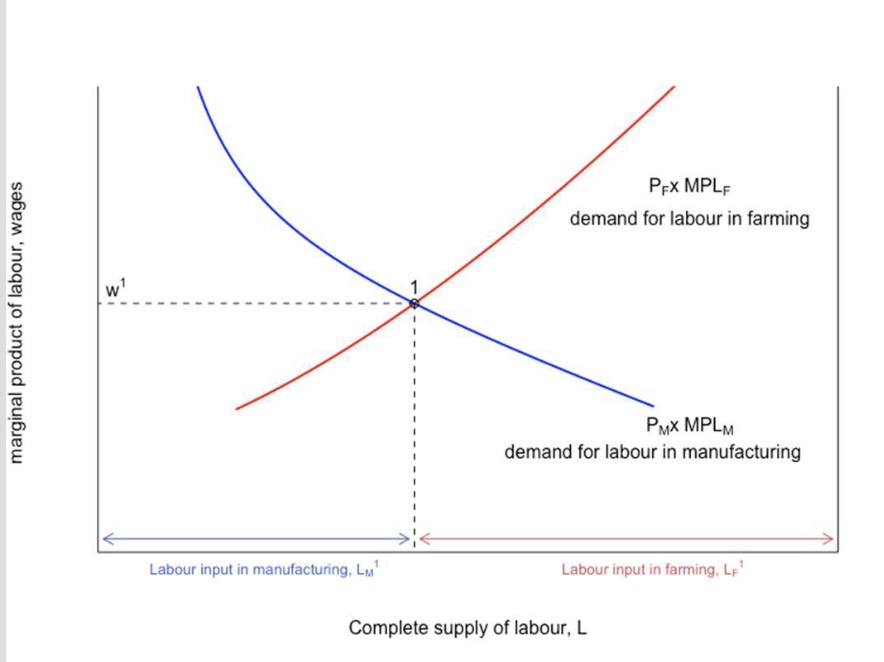
Shift of Price 50% upward of Good 1
w in the Sector 1 rises
Red Line shifts upward because of Formula
wage rise not exactly 50% but less because of Markets